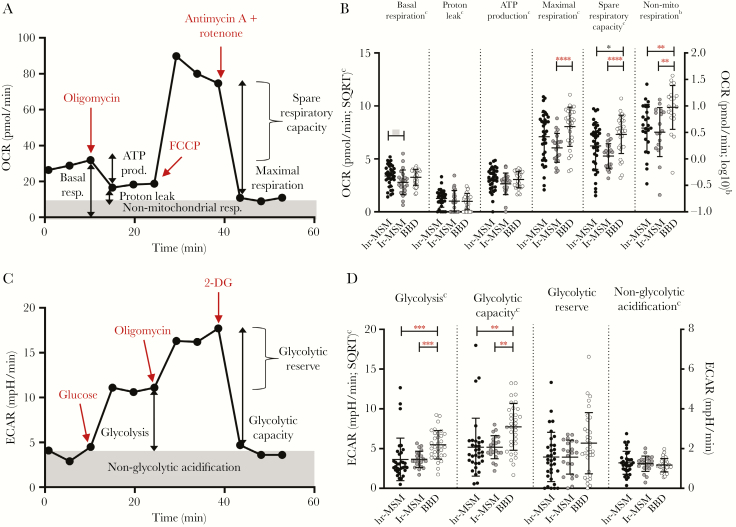
Figure 3.
Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from high-risk and low-risk men who have sex with men (MSM) and blood bank donors (BBD). (A) Overview of the bioenergetics profile, of 1 representative BBD, used to evaluate mitochondrial respiratory function of PBMCs from MSM with high-risk sexual behavior (hr-MSM), MSM without high-risk sexual behavior (lr-MSM), and BBD. A sequential addition of specific inhibitors and uncouplers (in red) of the electron transport chain provides data of the OCR relative to the different components of mitochondrial respiratory function. (B) The normalized OCR measured at different stages of the mitochondrial respiration, ie, basal respiration, proton leakage, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, maximal respiration, spare respiratory capacity, and nonmitochondrial respiration in the different study groups. (C) Overview of the bioenergetics profile, of a representative BBD, used to evaluate glycolytic function of PBMCs from hr-MSM, lr-MSM and BBD. A sequential addition of specific stimulators and inhibitors (in red) of glycolysis provides data of the ECAR relative to the different components of glycolytic function. (D) The normalized ECAR measured at different stages of the glycolysis pathway, ie, glycolysis, glycolytic capacity, glycolytic reserve, and nonglycolytic acidification in the different study groups: hr-MSM, n = 34; lr-MSM, n = 22; BBD, n = 31. Significance was assessed on normalized data with multivariable linear regression, corrected for age (*, P < .05; **, P < .01; ***, P < .001; ****, P < .0001; significance after Bonferroni correction in red and bold). Data represent mean ± standard deviation. Some individuals were excluded from analysis due to insufficient cell numbers. SQRT, square root.