Figure 7.
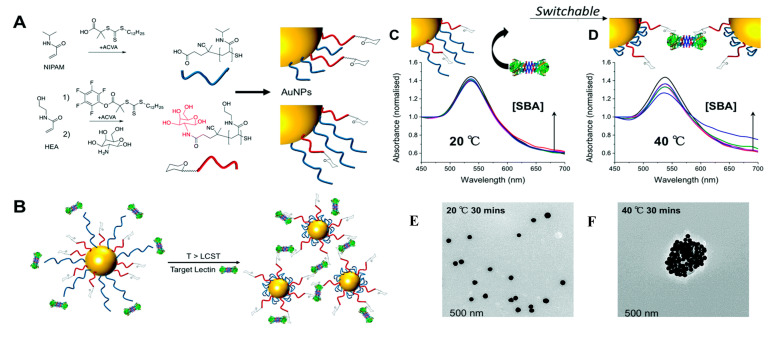
(A) Synthesis of polymers by RAFT (reversible activation fragmentation transfer); (B) concept of using responsive polymers to gate access to nanoparticles. Below the critical temperature longer polymer chain due to steric hindrance prevents lectin binding to glycans, but above the critical temperature, the polymer collapse to expose glycans enabling binding and aggregation of the particles. UV-Vis traces of different nanoparticle formulations in presence of serial dilution of lectin (1–10 μg·mL−1) after 30 min incubation at 20 °C (C) or 40 °C; (D). An increase in Abs700 and decrease in Abs540 is indicative of binding. All curves were normalized to Abs450 = 1. TEM images of these particles after addition of lectin (E) at 20 °C for 30 min; (F) at 40 °C following 30 min incubation. Reproduced with permission from [88]. Copyright Royal Society of Chemistry, 2017.