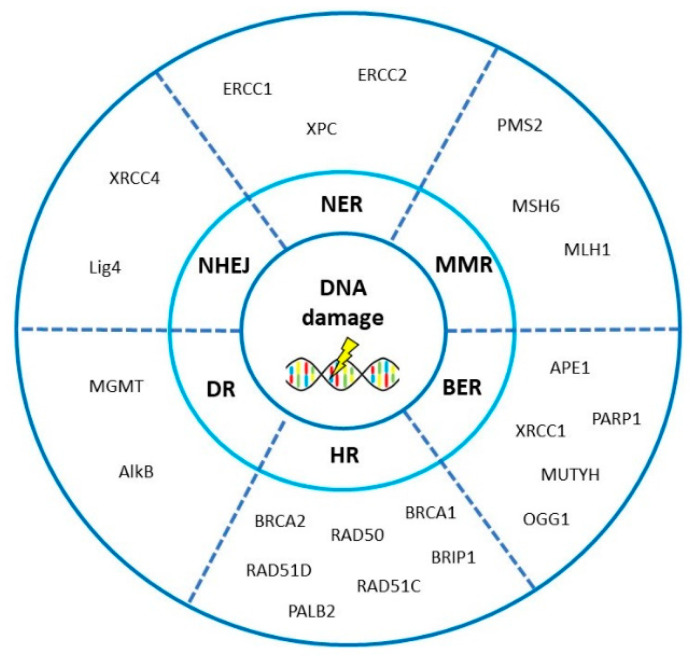
Figure 9.
The most important genes involved in DNA repair pathways in ovarian cancer. Scheme of DNA damage and the most important genes playing role in ovarian carcinogenesis, prognosis and therapy response NER (nucleotide excision repair), BER (base excision repair), NHEJ (non-homologous end-joining repair), MMR (mismatch repair), HR (homologous recombination), DR (direct repair)). Protein names: PMS1 homolog 2 (PMS2), MutS homolog 6 (MSH6), MutL homolog 1 (MLH1), apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1), poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1), X-ray repair cross-complementing 1 (XRCC1), MutY DNA glycosylase (MUTYH), 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1), breast cancer 1 and 2 (BRCA1 and 2), BRCA1-interacting protein C-terminal helicase (BRIP1), RAD50 homolog 1 (RAD50), RAD51 paralog C and paralog D (RAD51C and D), partner and localizer of BRCA2 (PALB2), alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase AlkB (AlkB), O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), DNA ligase 4 (LIG4), X-ray repair cross-complementing 4 (XRCC4), excision repair cross-complementation group 1 (ERCC1), xeroderma pigmentosum complementation protein C and D (XPC and D/ERCC2).