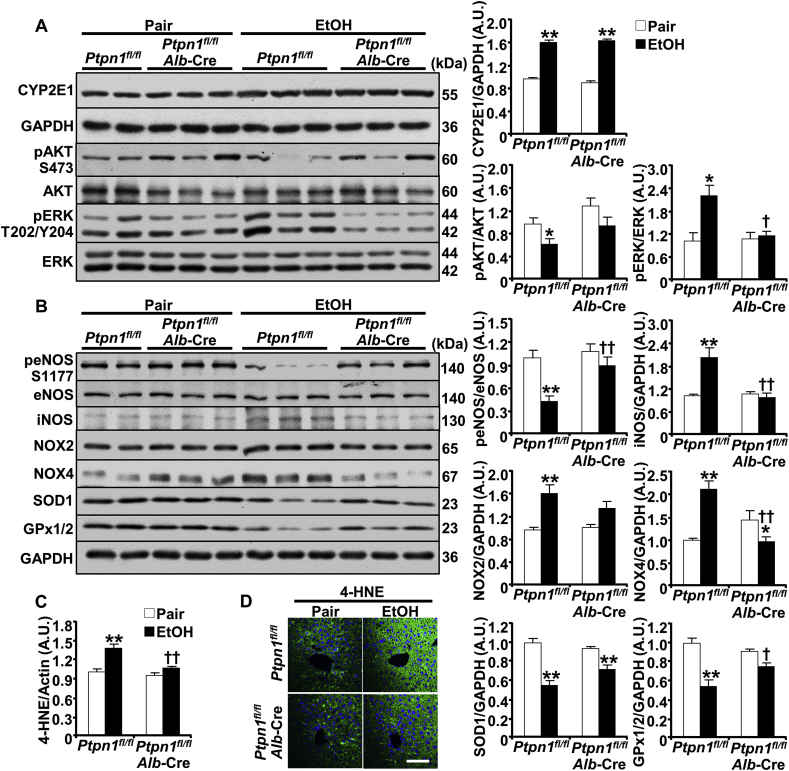
Fig. 4.
Hepatic PTP1B disruption is associated with decreased ethanol-induced oxidative stress. Ctrl (Ptpn1fl/fl) and KO (Ptpn1fl/fl, Alb-Cre) female mice were used in the chronic plus binge model. Pair: control diet + maltose gavage, EtOH: ethanol diet + ethanol gavage. Immunoblots of (A) CYP2E1, pAKT, AKT, pERK, ERK and GAPDH, and (B) peNOS, eNOS, iNOS, NOX2, NOX4, SOD1, GPx1/2, and GAPDH in mouse liver lysates (left panels). Each lane represents an independent animal. Protein expression of CYP2E1, iNOS, NOX2, NOX4, SOD1, and GPx1/2 was normalized with GAPDH. Phosphorylation of AKT, ERK, and eNOS was normalized with their respective protein. C) Lipid peroxidation was determined by immunoblotting liver lysates with 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) then quantitated (full lane intensity of 4-HNE immunoblot was normalized with Actin), as well as immunostaining of liver sections (D). All quantitative results were plotted as means + SEM (n = 5 pair-fed Ctrl mice and n = 6 for each of the remaining groups). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 Pair vs. EtOH and †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 Ctrl vs. KO by a two-tailed t-test (A), and One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey's test (B, C). A.U.: arbitrary unit. Scale bar: 50 μm.