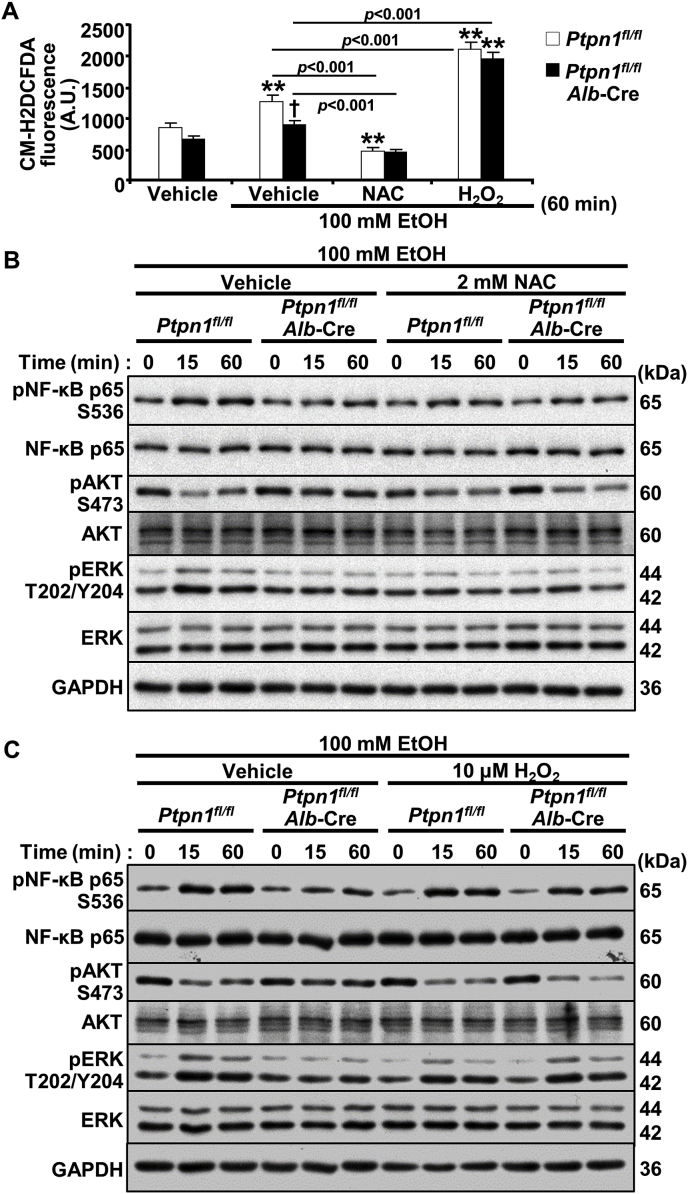
Fig. 5.
PTP1B disruption modulates oxidative stress signaling in ethanol-treated hepatocytes. Primary hepatocytes isolated from Ctrl (Ptpn1fl/fl) and KO (Ptpn1fl/fl, Alb-Cre) male mice were incubated without and with 100 mM ethanol (EtOH) plus 2 mM N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and 10 μM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as indicated. A) Intracellular ROS levels as measured by CM-H2DCFDA upon EtOH stimulation and with interventions of NAC and H2O2 for 60 min. The CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence was plotted in the bar chart as means + SEM. **p < 0.01 without vs. with EtOH and †p < 0.05 Ctrl vs. KO. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey's test. A.U.: arbitrary unit. Immunoblots of pNF-κB, NF-κB, pAKT, AKT, pERK, ERK, and GAPDH in lysates from hepatocytes co-treated with EtOH and NAC (B) or H2O2 (C) for the indicated periods.