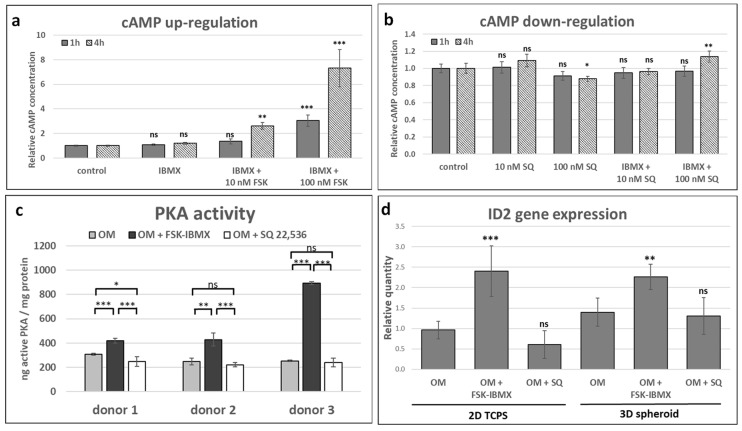
Figure 2.
Effect of adenylate cyclase regulation on cAMP pathway activity. Cells cultured in OM and treated with adenylate cyclase activator forskolin (FSK, concentration of 10 nM unless indicated otherwise) and phosphodiesterase inhibitor 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX, 500 nM), or with adenylate cyclase inhibitor SQ 22,536 (100 nM unless indicated otherwise). Analysis of intracellular cAMP under cAMP (a) upregulation and (b) downregulation. Cells in suspension treated with regulator for 1 or 4 h, and each treated sample contained 5000 cells. Relative cAMP concentration, normalized to control sample, is shown. (a,b) Mean from three experiments performed on cells isolated from a single donor, error bars represent standard deviation. (c) protein kinase A (PKA) activity assay. Cells cultured with regulators for 48 h. PKA activity shown as ng of active PKA enzyme, normalized to the amount of total protein in sample. Mean from three experiments performed on cells isolated from different donors; results from each cell donor separately presented, error bars represent standard deviation. (d) Relative expression of ID2 gene, cyclic–AMP response element binding protein (CREB) target gene. Cells cultured with regulators for 48 h. Mean from three experiments performed on cells isolated from different donors. Control, undifferentiated cells; “0”, cells cultured in OM without regulators. Error bars, ±95% confidence interval. Statistical significance between control or OM and adenylate cyclase regulation conditions is marked: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant.