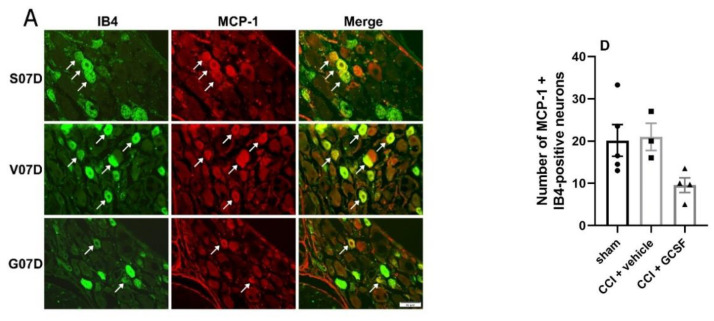
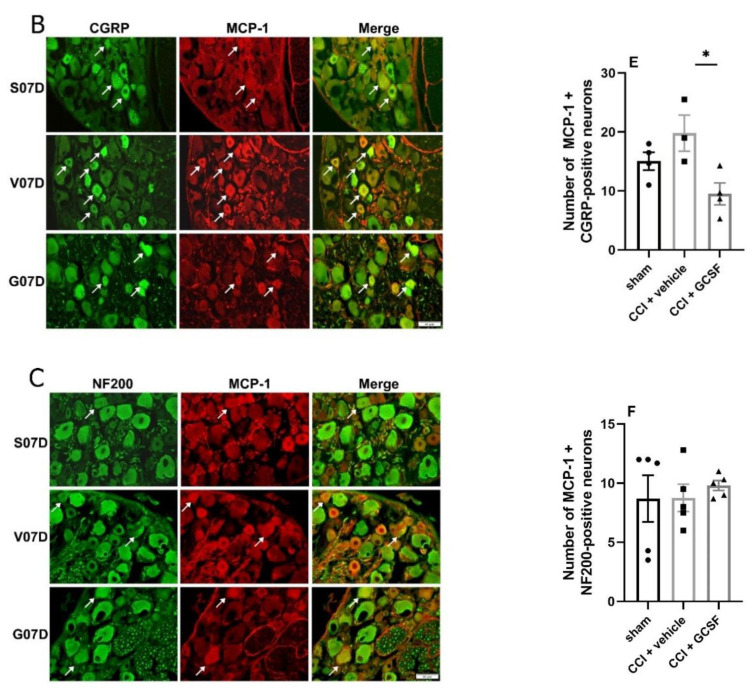
Figure 7.
GCSF treatment decreased the number of MCP-1 + CGRP-positive neurons in the DRGs of CCI rats (B,E). Immunohistochemical studies revealed that many MCP-1-positive neurons (red) in the DRGs were co-stained with IB4 (green (A), a marker of small-diameter, C-fiber nonpeptidergic sensory neurons), CGRP (green (B), a marker of small- to medium-diameter peptidergic sensory neurons), and NF200 (green (C), a marker of large-diameter myelinated sensory neurons) (Figure 7A–C). Significantly fewer MCP-1 + CGRP-positive neurons were observed in the DRGs of the GCSF-treated CCI rats than in the DRGs of the vehicle-treated CCI rats on the 7th day after nerve injury (E). There was a tendency for the GCSF-treated CCI rats to exhibit fewer MCP-1+ IB4-positive neurons in the DRGs than the vehicle-treated CCI rats and sham-operated rats. However, the differences were not statistically significant (D). In contrast, there were no significant differences in the number of MCP-1 + NF200-positive neurons in the DRGs between the different groups (F) (one-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey’s test or Kruskal–Wallis, post hoc Mann–Whitney rank-sum test, if appropriate; Day 7: n = 4 per group). Scale bars = 50 μm. The arrows indicate MCP-1-positive/IB4-positive, MCP-1-positive/CGRP-positive, and MCP-1-positive/NF200-positive neurons. * p < 0.05.