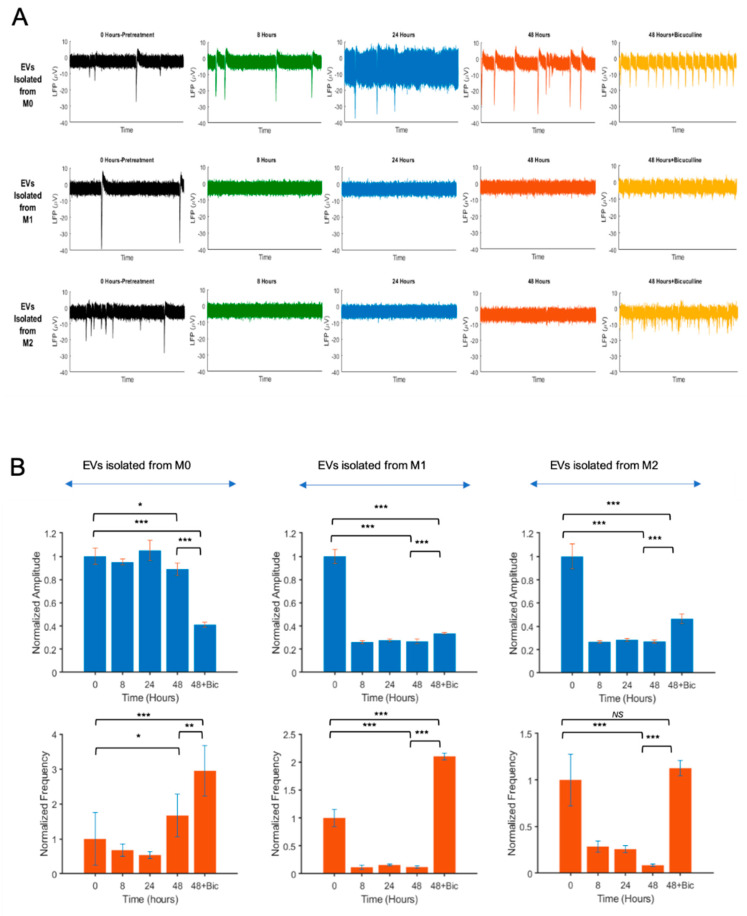
Figure 5.
Effect of EVs isolated from M0, M1, and M2 on neuronal activity by microelectrode array studies (MEA). (A) Extracellular action potential recordings of primary rat neurons treated with EVs from M0, M1, and M2 macrophages. Rat hippocampal neurons were dissociated from the hippocampi of E18 prenatal rat embryos and placed onto the MEA dishes. Experimental recordings and EV treatments were started when the cultures were 21 days old. After placing the MEAs on the amplifier, recordings were performed using the MC_Rack software. The recorded electrophysiological activities are shown for a 60-s duration of the recordings. The recorded spiking data (in μV versus time) were transferred to the MATLAB environment for further offline analysis. Top row: M0-Evs at t = 0, 8, 24, and 48 h. Middle row: M1-EVs treated neurons at t = 0, 8, 24, and 48 h. Bottom row: M2-EVs treated neurons at t = 0, 8, 24, and 48 h. At 48 h posttreatments, cells were also treated with bicuculline and recorded. (B) Time-dependent variations of the normalized firing frequency and amplitude of cells treated with EVs isolated from M0, M1, and M2 macrophages are shown as bar graphs. (n = 3; * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, and *** p ≤ 0.001).