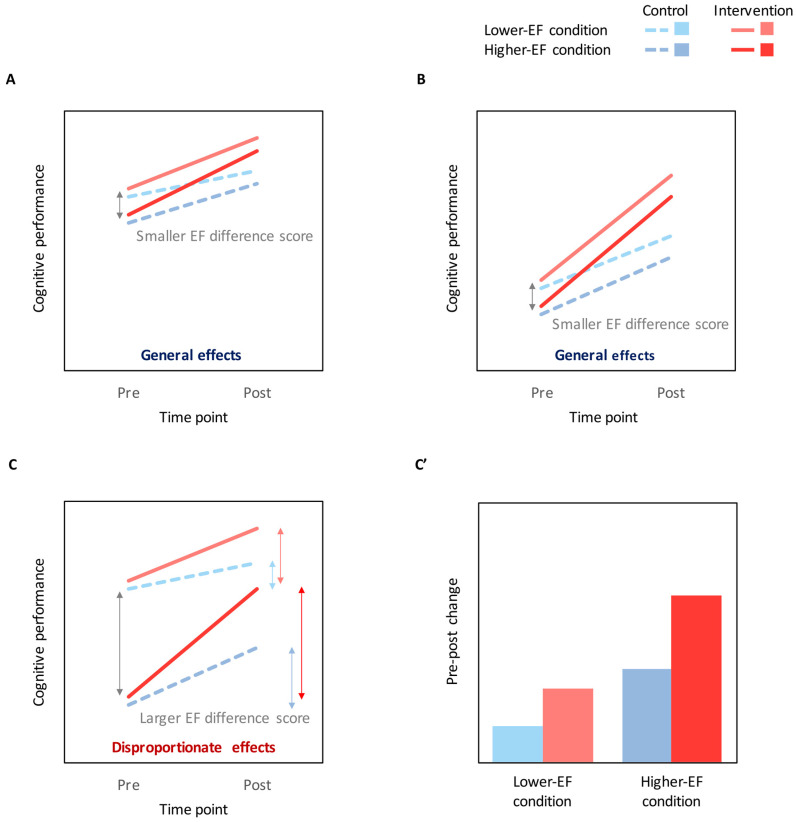
Figure 2.
Conceptual diagrams of the prediction of changes in cognitive performance based on the baseline EF (executive function) difference scores. (A) If baseline cognitive performance is relatively high in both the lower-EF and higher-EF conditions (i.e., smaller EF difference score), cognitive improvements resulting from a PA intervention would be relatively small in the both EF conditions, resulting in the general effects of PA on cognitive performance irrespective of EF conditions. (B) If baseline cognitive performance is relatively low in the both EF conditions (i.e., smaller EF difference score), cognitive improvements resulting from a PA intervention would be relatively large in the both EF conditions, resulting in the general effects. (C) If the baseline EF difference score is sufficiently large, cognitive improvements resulting from a PA intervention would be greater for the higher-EF condition relative to the lower-EF condition, resulting in the disproportionate effects. Colored double-headed arrows show pre–post changes in cognitive performance (i.e., the present dependent variable) in each group and EF condition. (C’) The line graph in (C) is converted to a bar graph using the pre–post changes in cognitive performance in accord with Figure 3B.