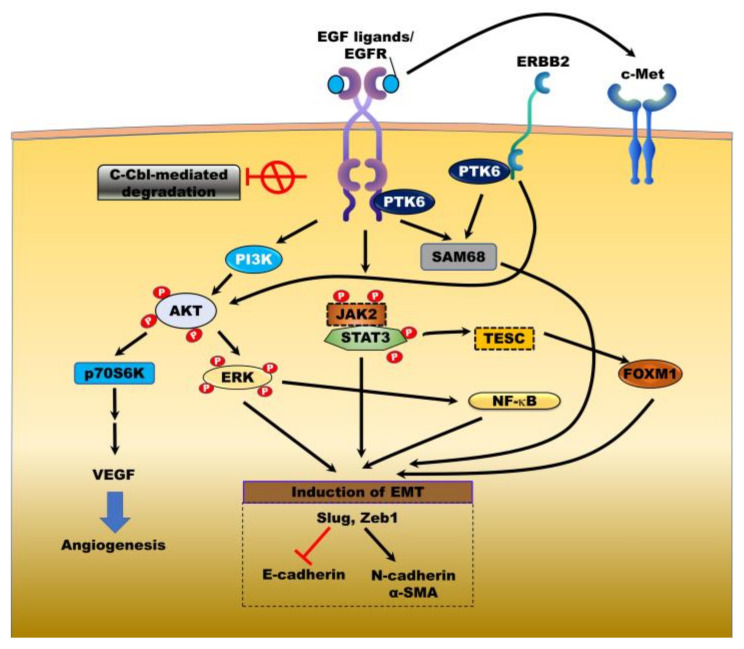
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of the EGFR family signaling in cholangiocarcinoma. ErBb family leads to tumor growth, vascularization, tumorigenesis, and metastasis through ligand-mediated activation of downstream targets and other transmembrane receptors, c-Met. Inhibition of c-cbl-mediated degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) enhances accumulation and activation of EGFR and then activates the downstream signaling pathways and contribute to angiogenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transmission (EMT) program by induction of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and EMT transcription factors (EMT-TF’s). JAK2: Janus kinase 2, STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, SAM68: KH RNA binding domain containing, signal transduction associated 1, PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, ERK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase, VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor, NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B, FOXM1: Forkhead box M1, TESC: Tescalcin, Slug: Snail family transcriptional repressor 2, Zeb1: Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1, PTK6: Protein tyrosine kinase 6.