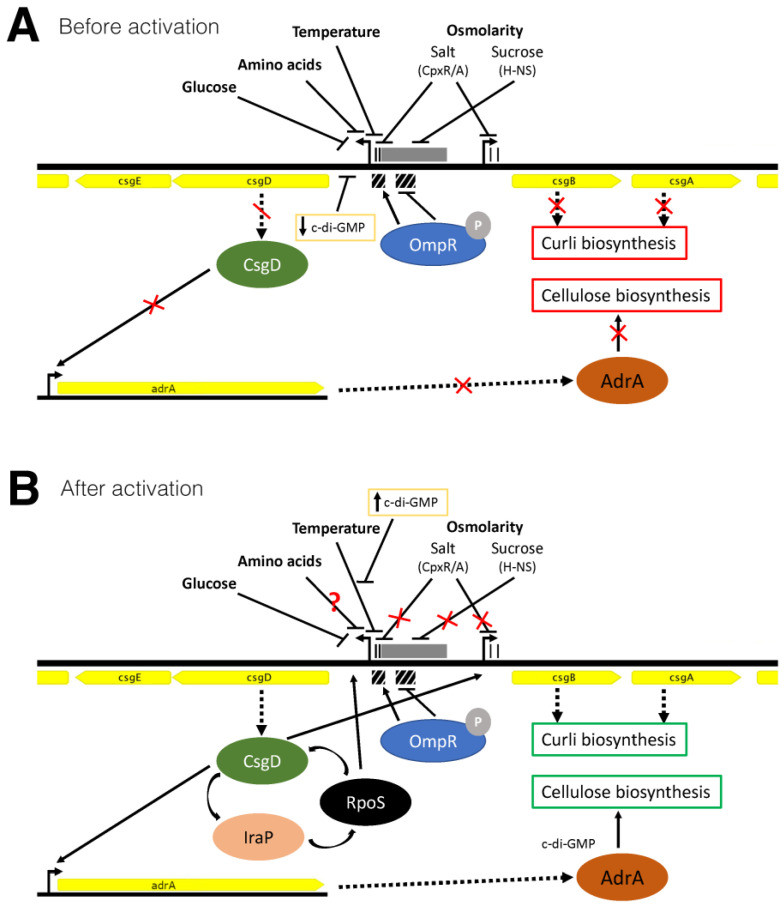
Figure 8.
Graphical illustration of the CsgD regulatory principles identified in this manuscript. The divergent csg operons are shown (without csgFG and csgC) with the intergenic region highlighted by transcription factor binding sites that have been experimentally verified in Salmonella (CpxR—black bars; H-NS—grey box; OmpR—hatched boxes). Phosphorylated OmpR binds the proximal, high affinity site under conditions of low osmolarity, which activates csgD transcription, and binds the distal, low affinity sites under conditions of high osmolarity, which represses csgD transcription [38]. The different regulatory elements that we have tested are shown: glucose; amino acids; growth temperature; and osmolarity, with sodium chloride, which is known to act via the CpxR/A system [37], and sucrose, which is known to act via H-NS [36]. The adrA gene encodes a diguanylate cyclase, which produces cyclic-di-GMP and allosterically activates cellulose production. (A) Glucose (>25 mM), amino acids (>0.5% casamino acids), temperature (>32 °C), salt and sucrose (>25 mM) caused a reduction in csgD transcription and blocked transcription of csgBAC and adrA, preventing curli and cellulose biosynthesis. The effect of reduced c-di-GMP was tested by overexpression of the YhjH phosphodiesterase. The addition of individual amino acids was variable, with three leading to reduced csgD transcription (Asn, Pro, Arg), and seven leading to increased csgD transcription (Ile, Val, Gln, Met, Ala, Thr, Gly). (B) When the same regulatory components were tested after 18 h of growth, the effects were different. We assume that by this time point, the CsgD-IraP-RpoS feed-forward loop [35] is activated, although deletion of iraP in our experiments had little effect. The addition of salt and sucrose had no effect on csgD transcription, and casamino acids were not as repressive. The effect of increased c-di-GMP was tested by overexpression of the diguanylate cyclase STM1987, which was able to relieve temperature-based repression of csgD transcription. The response to individual amino acids was again variable, however, none caused a reduction in csgD transcription and eight were stimulatory (Leu, Arg, His, Val, Pro, Ala, Gln, Thr). The question mark signifies that we do not fully understand the regulatory effects of individual amino acids.