FIGURE 6.
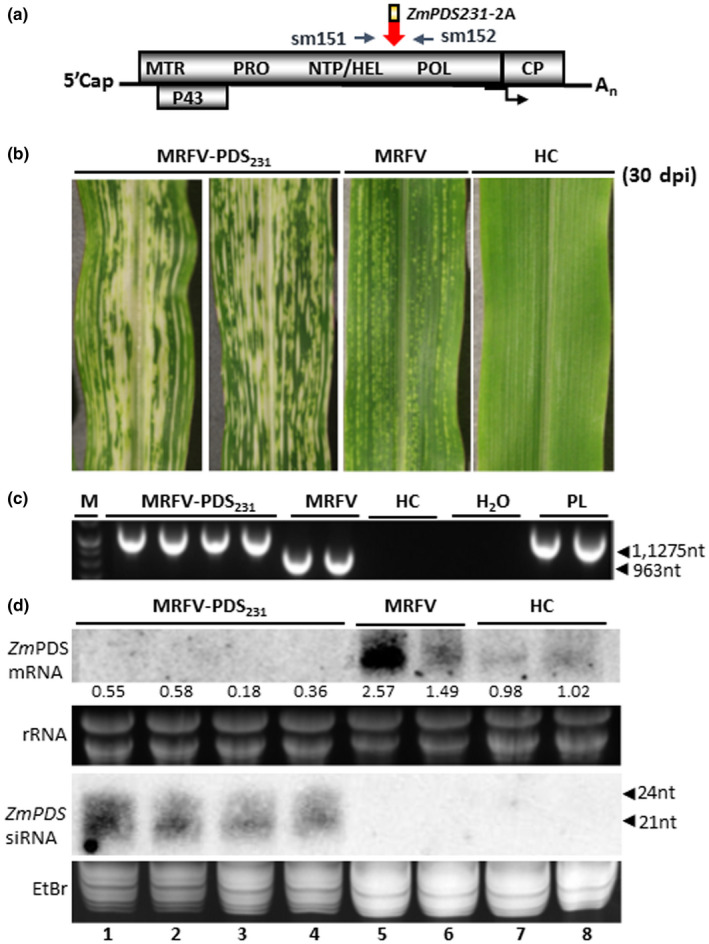
Capacity of HEL/POL junction to hold larger inserts. (a) Similar to MRFV‐PDS120, molecular assays for MRFV‐PDS231 used primers sm151 and 152 for RT‐PCR detection, amplifying 1,275 bp in MRFV‐PDS231 and 963bp in MRFV‐WT. (b) Virus symptoms and chlorophyll photobleaching phenotype induced by MRFV‐PDS231 at 30 dpi, compared to MRFV‐WT and noninoculated plants. (c) RT‐PCR analysis of virus accumulation in systemic leaves at 30 dpi. The gel shows RT‐PCR detection of MRFV‐PDS231 and MRFV‐WT in systemic leaves of inoculated plants. Healthy plants (HC) and water (H2O) were included as negative controls and the MRFV‐PDS231 plasmid (PL) as a positive control. M: 100 bp DNA marker. (d) Northern blot analysis of photobleaching phenotype induced by MRFV‐PDS231 was as described in Figure 3. Levels of PDS mRNA and siRNAs from MRFV‐PDS231‐infected leaves is shown (lanes 1–4) compared to MRFV‐infected (lanes 5–6) and healthy plants (lanes 7–8). The relative levels of PDS mRNA were determined as described in Figure 3
