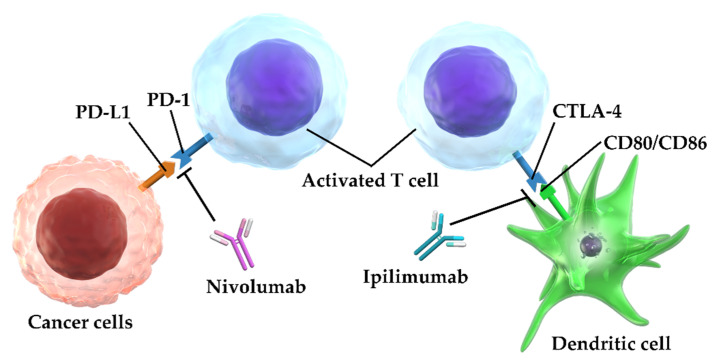
Figure 10.
Ipilimumab releases T lymphocytes from suppression caused by CD80/CD86-expressing dendritic cells by competing for binding to CTLA-4 on T lymphocytes, and induces T lymphocyte activation and proliferation. Nivolumab releases T lymphocytes from suppression caused by PD-L1-expressing cancer cells by binding to the PD-1 molecule. These properties of ipilimumab and nivolumab contribute to the restoration of the antitumor effect of T lymphocytes; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4.