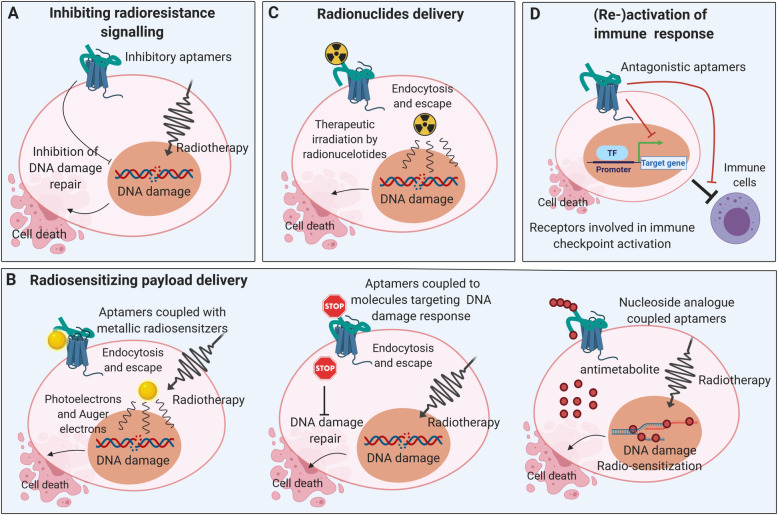
Fig. 2.
Different strategies of aptamer-based combined modality approach with radiotherapy. Aptamers specifically bind to the target structures (e.g. EGFR, PSMA, MUC-1, nucleolin, etc.), endocytosed and released in the cytoplasm following lysosomal degradation (a) Aptamer-binding to designated target interferes with radio-resistance signaling and sensitize radiotherapy. b Several radiosensitizers, such as metal formulations, siRNAs and nucleoside analogs can be coupled with aptamers for targeted delivery into cancer cells to sensitize radiotherapy. c Therapeutic radionuclides can be incorporated into aptamers for targeted radiotherapy. d These aptamers (re-)activate systemic anti-tumor immune responses by targeting immune checkpoint activation related receptors, enable antitumoral immunity and possible abscopal effects