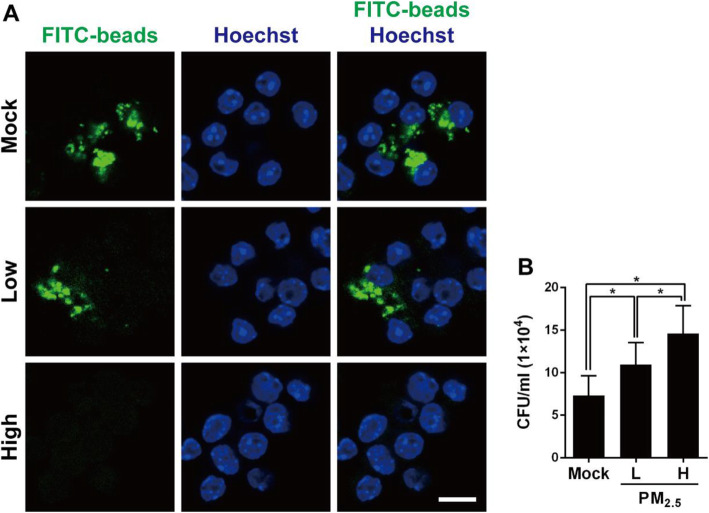
Fig. 2.
PM2.5 suppresses macrophage phagocytosis in response to pneumococcal infection. a RAW264.7 cells were exposed to low (5 μg/ml) or high (20 μg/ml) doses of PM2.5 for 24 h, and then incubated with latex fluorescent beads for 3 h. The nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 and the image was analyzed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. b RAW264.7 cells were exposed to low or high doses of PM2.5 for 24 h before pneumococcal infection for 6 h (MOI = 10). Intracellular pneumococcal survival was determined using gentamicin protection assays and expressed as viable CFU. Results are represented mean ± standard deviation from triplicate independent experiments and P-value was determined by using one-way ANOVA followed by a post-hoc test (*, P < 0.05)