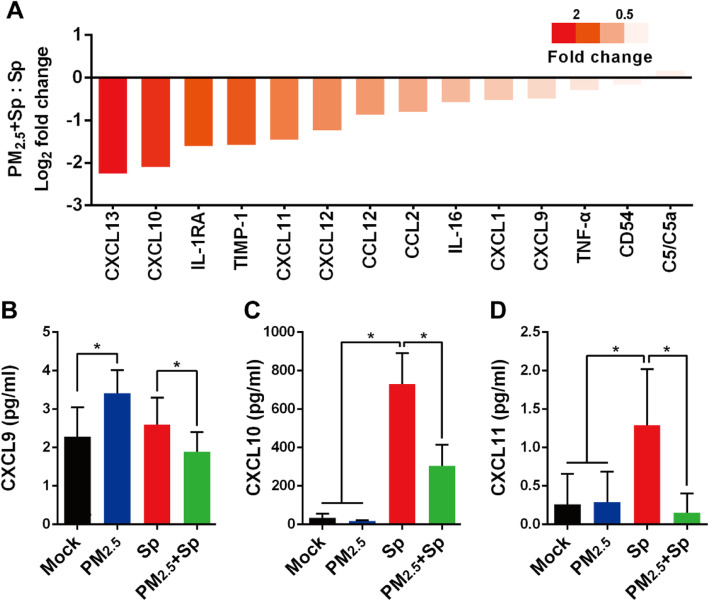
Fig. 6.
PM2.5 inhibits pneumococcus-induced chemokine production. a Mice were administered PM2.5 and infected with pneumococcus, as described in Fig. 4. After euthanizing the mice, the collected BALF collected from mice (n = 6) was pooled into one sample and subjected to cytokine array analysis. Chemokine expression was quantified using ImageJ. Log2 fold changes were calculated for the PM2.5 + pneumococcus co-treated and only pneumococcus-infected groups. RAW264.7 cells were incubated with or without 20 μg/ml PM2.5 for 24 h, and pneumococcus-infected or uninfected for 6 h. Culture supernatant was collected, and the concentrations of (b) CXCL9, (c) CXCL10, and (d) CXCL11 were determined using ELISA. Statistical significance was analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by a post-hoc test (*, P < 0.05)