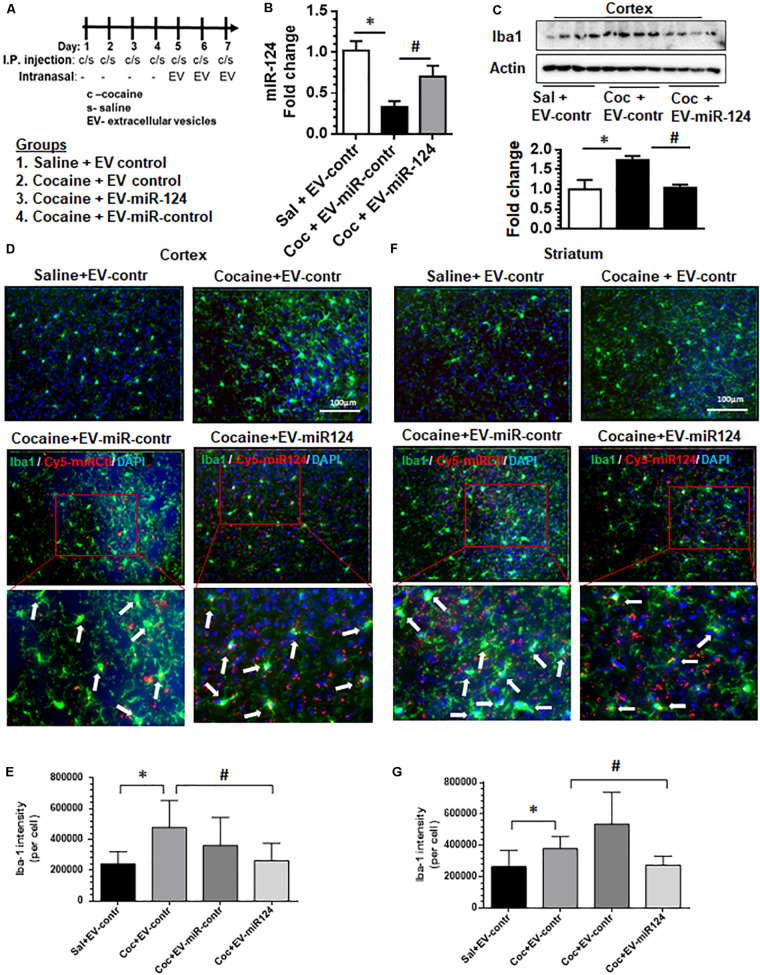
FIGURE 3.
Intranasal delivery of dendritic cell-derived EVs loaded with Cy5-miR-124 inhibits cocaine-mediated upregulation of Iba-1 in vivo. Wild-type C57BL/6N mice were administered cocaine (20 mg/kg; i.p.) or saline for seven consecutive days. On the fifth, sixth and seventh days, mice were intranasally administered dendritic cell-derived EVs loaded with Cy5-miR-124 or Cy5-scrambled miRNA or were left unloaded, followed by cocaine injections (i.p.). (A) Scheme for intranasal administration of EVs and cocaine injections. (B) Expression levels of miR-124 in the cortex. (C) Western blot for Iba1 in the cortex. Actin served as a loading control. (D) Representative immunofluorescence staining images for Iba1 in mice cortical sections from the four groups of mice i.e., saline + control EVs; cocaine + control EVs; cocaine + EV-Cy5-scrambled miRNA (sham); cocaine + EV-Cy5-miR-124. The blown-out sections show Iba1+cy5+ microglial cells indicated by arrows. (E) Quantification of Iba1 fluorescence intensity normalized to the number of Iba1+ cells in the cortex. (F) Representative immunofluorescence staining images for Iba-1 in the striatum from the four groups of mice. (G) Quantification of Iba1 fluorescence intensity intensity normalized to the number of Iba1+ cells in the striatum. (n = 4/group, ∗p < 0.05 vs. saline+ EV control, #p < 0.05 vs. cocaine+ EV control group, one way ANOVA, Turkey’s multiple comparisons test).