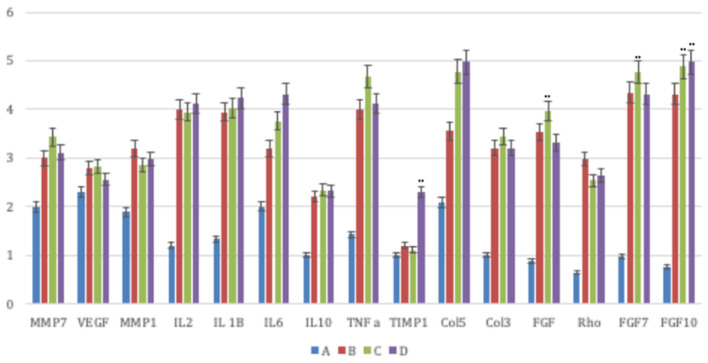
Figure 5.
The principal molecules involved in the wound healing process were investigated by means of a real-time PCR array analysis in all groups (Group A: control lesions; Group B: 16 mg/ml talc injection; Group C: 160 mg/ml talc injection; Group D: 300 mg/ml talc injection) at 4 weeks. Regarding the ECM components, the treated samples showed a greater expression of collagens (type 5 and 3 mRNA) compared to control. Concerning the remodeling enzymes, all matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) displayed a significant increase. Concerning the inflammatory cytokines the treated samples exhibited a greater expression of inflammatory interleukin (IL) 1 and a lesser expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL10). Moreover, they showed high levels of growth factor transcripts, such as the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 7, FGF10, transforming growth factor (TGF) A, TGFB1, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Repeated-measures ANOVA with a post-hoc analysis using Bonferroni's multiple comparison. T tests were used to determine significant differences (p < 0.05). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Repeatability was calculated as the standard deviation of the difference between measurements.