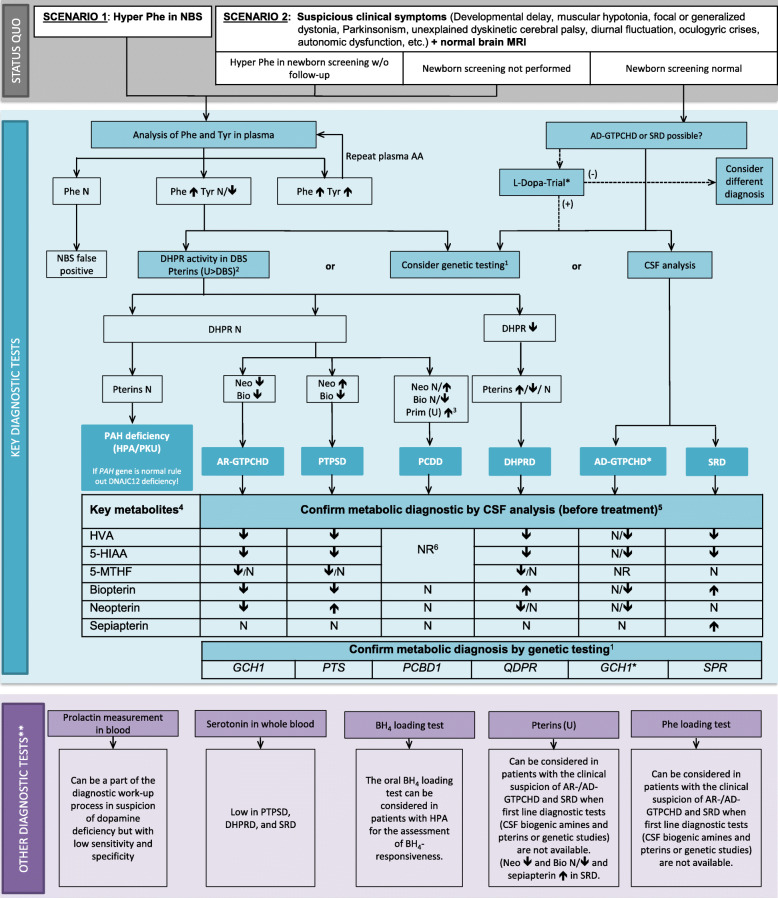
Fig. 2.
Diagnostic flowchart for differential diagnosis of BH4Ds with and without HPA. 1Consider genetic HPA workup depending on availability and financial resources. The gene panel should include the QDPR, GCH1, PTS PCBD1, SPR genes as well as DNAJC12. For GCH1, consider MLPA if Sanger sequencing is negative. 2The analysis in urine is more sensitive than in DBS and pathological patterns suggestive for PCDD and SRD can only be detected in urine but not in DBS. 3Primapterin measurement in urine is only elevated in PCDD. 4Aminoacids in CSF are not required for diagnosis of BH4Ds. 5CSF analysis should always include standard measurements (cell count, proteins, glucose and lactate). 6Recommendation against measurements of HVA, 5-HIAA, 5-MTHF, and pterins in CSF in the case of PCDD. (*) A diagnostic L-Dopa trial should be limited to children with symptoms suggestive of dopa-responsive dystonia or to situations where biochemical and genetic diagnostic tools are not available. If the diagnostic L-Dopa trial is positive but the results of CSF biochemical and/or molecular genetic testing are not compatible with AD-GTPCHD or SRD, further aetiologies for dopa responsive dystonia should be considered (e.g. juvenile parkinsonism (PARK2gene)). (**) Can be considered if available. See text for more detailed information. Abbreviations: 5-HIAA, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid; 5-MTHF, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate; AA: amino acids; AD−/AR- GTPCHD: guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase I deficiency; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; Bio: biopterin; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; DBS: dry blood spot; DHPR: q-dihydropteridine reductase; DHPRD, dihydropteridine reductase deficiency; HVA, homovanillic acid; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; N: normal; NBS: newborn screening; Neo: neopterin; NR: not reported; PAH: phenylalanine hydroxylase; Phe: phenylalanine; PKU: phenylketonuria; Prim: primapterin; PTPSD, 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase deficiency; SRD: sepiapterin reductase deficiency; Tyr: tyrosine; u: urine; (+) = positive effect; (−) = no or no clear effect