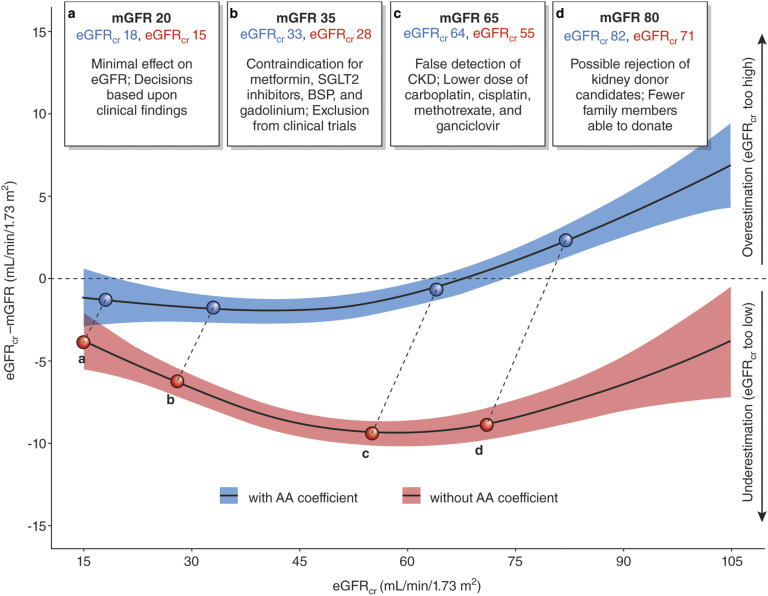
Figure 1.
Clinical decisions can be affected by accuracy of GFR assessment among blacks. Data from 2601 black participants from the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration development and internal validation sample were used in this plot (28). We computed eGFR from serum creatinine (eGFRcr) values with (blue) and without (red) the application of the black coefficient and removed values below and above the 2.5 and 97.5 percentiles of these distributions, leaving 2463 participants for the analysis. The model plotted represents generalized additive models for eGFRcr (milliliters per minute per 1.73 m2) on the difference between eGFRcr and measured GFR (mGFR) (milliliters per minute per 1.73 m2). We truncated the horizontal axis to eGFRcr values from 15 to 105 ml/min per 1.73 m2, excluding 190 participants from the plot. The colored areas along the line represent 95% confidence intervals of the estimate. Upper boxes represent hypothetical situations of eGFRcr values for the same mGFR, with numbers in blue representing the eGFRcr with the black coefficient and the numbers in red representing the eGFRcr without the black coefficient. AA, black; BSP, bisphosphonate; SGLT2, sodium-glucose transport protein 2. Modified from ref. 72, with permission.