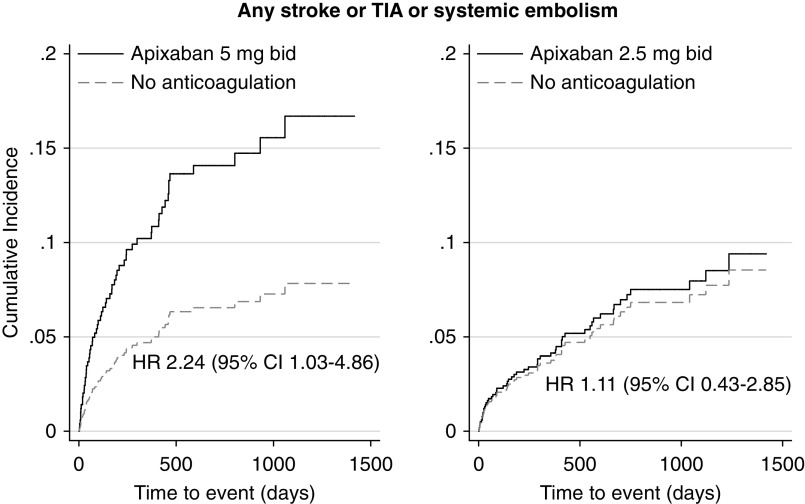
Figure 2.
A significantly higher incidence of any stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or systemic thromboembolism was seen in the subgroup of patients treated with the standard apixaban dose but not in patients who received the reduced apixaban dose, compared with patients who did not receive any anticoagulants. Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) are depicted. Death was considered as competing risk. Apixaban prescription was examined as a time-varying covariate. bid, twice daily; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.