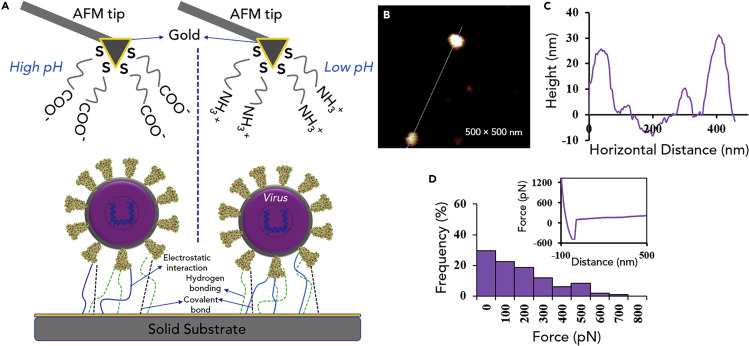
Figure 4.
The AFM Technique to Investigate the Interactions of the Virus with a Solid Surface
(A) Overview of AFM probe functionalization and virus adsorption onto a solid surface. AFM tips can be negatively or positively charged through either deprotonation of carboxyl group leading to carboxylate anion formation at high pH environment or protonation of amine functional group at low pH environment, respectively.
(B) AFM to measure virus surface chemistry. AFM image of bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) attached to a glass slide and the hydrophobicity was measured with a methyl-terminated AFM tip.
(C) Corresponding height image of the line in (B). The virus was found to be the size of known BVDV particles.
(D) The frequency of different forces found from pulling on BVDV particles with a methyl-terminated AFM tip. The histogram represents >300 force-distance curves using a combination of 3 different functionalized tips and 3 different batches of virus. The spring constant for the tip was 0.07–0.15 N/m. The mean force was 221 pN. The insert is a representative force distance curve. BVDV is an enveloped virus with size range of 40–60 nm and related to the hepatitis C human virus.