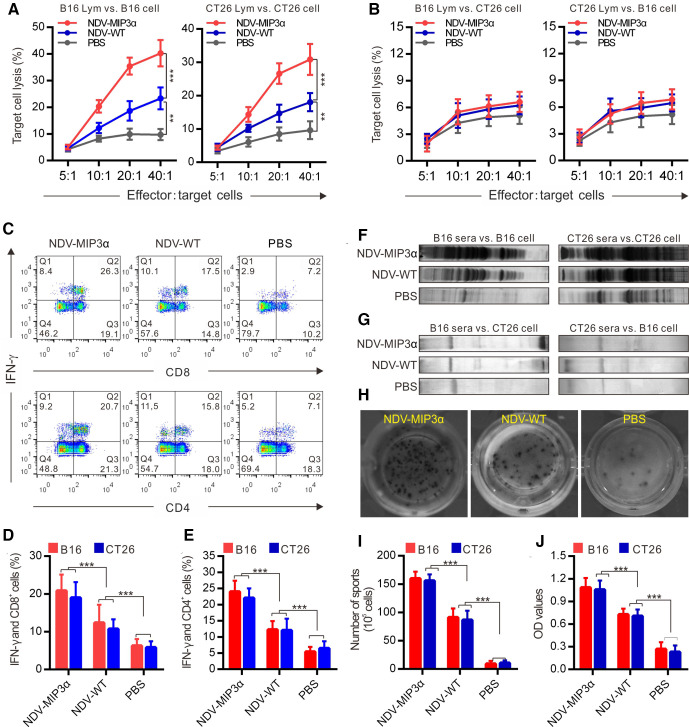
Figure 5.
NDV-MIP3α induces stronger tumor-specific cellular and humoral immune responses than the NDV-WT. (A) CTL responses were performed using cells from B16-bearing or CT26-bearing mice treated with the indicated formulations as effector cells, and the B16 or CT26 tumor cells as target cells, respectively. (B) CTL responses using the splenic lymphocytes (Lym) as effector cells, but oppositive tumor cells (B16 Lym vs CT26 and CT26 Lym vs B16) as target cells. (C) The representative images of FCM analyzed IFN-γ-secreted CD4+ and CD8+ splenic lymphocytes, respectively. (D) The data of four independent experiments of FCM show the percentage of IFN-γ-secreting CD8+ lymphocytes. (E) The data of four independent experiments of FCM show the percentage of IFN-γ-secreting CD4+ lymphocytes. (F) Western blot using sera IgG from B16-bearing or CT26-bearing mice treated with the indicated formulations against the B16 or CT26 tumor lysates, respectively. (G) Western blot using sera IgG from B16-bearing or CT26-bearing mice against oppositive tumor lysates (B16 sera vs CT26 lysates and CT26 sera vs B16 lysates). (H) The representative images of ELISPOT assay of lymphocytes secreting specific IgG antibodies against B16 cells. (I) The number of lymphocytes secreting IgG antibodies against B16 and CT26 tumor cells detected by ELISPOT assay. (J) The titers of sera IgG specific to B16 and CT26 tumor lysates from mice treated with the indicated formulations detected by ELISA. Data are plotted as mean±SD, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; ELISPOT, enzyme-linked immunospot; FCM, flow cytometry; MIP-3α, macrophage inflammatory protein-3α; NDV, Newcastle disease virus; NDV-WT, wild-type NDV.