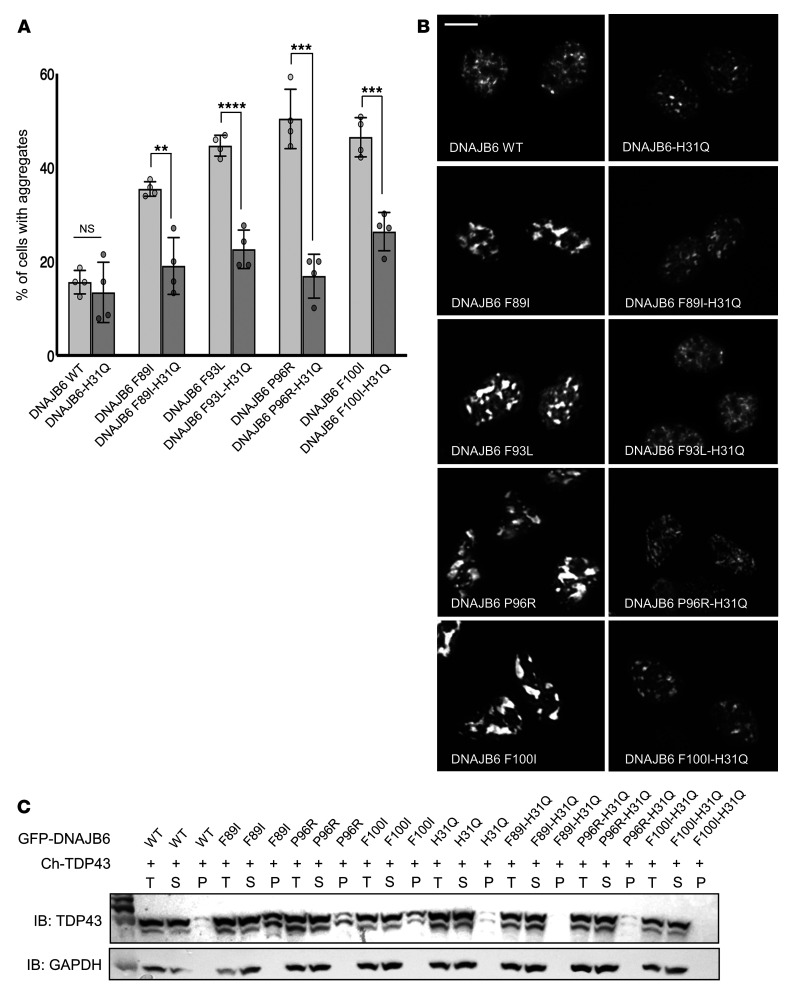
Figure 2. LGMDD1 mutations in DNAJB6b impair TDP43 disaggregation, which is corrected with a second H31Q mutation.
(A–C) HeLa cells were cotransfected with mCherry-TDP43 and WT or LGMDD1-mutant (F89I, F93L, P96R, or F100I) GFP-DNAJB6b. In some cases, a second mutation in the J domain (H31Q) was also present. Transfected cells were heat shocked at 42°C for 1 hour before analysis. (A) Quantification of the percentage of transfected cells with TDP43 aggregates. **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, and ****P < 0.00005, by paired Student’s t test for comparisons between groups; a 1-way between-conditions ANOVA was performed to compare the effects of mutations. There was a significant effect at P < 0.05 for the 5 conditions [F(4,15) = 54.5, P = 9.3 × 10–9]. n = 300 cells analyzed per condition; the experiment was conducted 3 times. (B) Representative fluorescence images of the mCherry-TDP43–positive nuclei quantified in A. Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Lysates from cells in A were separated into total (T), soluble (S), and pellet (P) fractions and then subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-TDP43 and anti-GAPDH antibodies. The immunoblot (IB) is representative of 3 independent experiments. Ch-TDP43, mCherry-tagged TDP43.