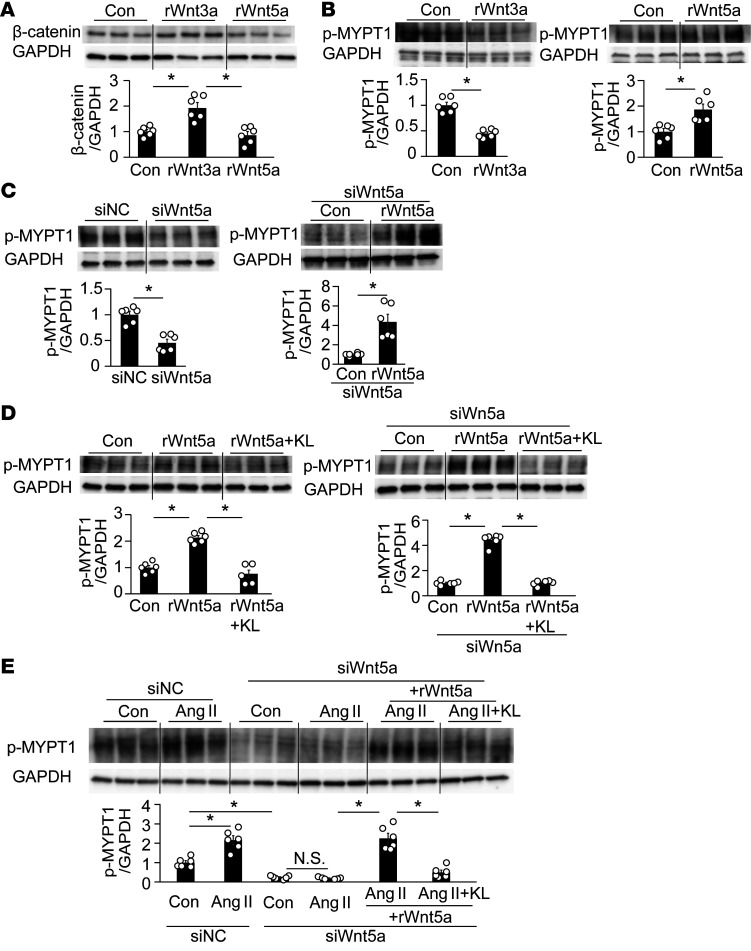
Figure 6. Wnt5a- and Ang II–induced upregulation of p-MYPT1 in cultured human VSMCs.
(A) Recombinant (r) Wnt3a increased active β-catenin expression in cultured hVSMCs, but rWnt5a did not. n = 6 each. *P < 0.05 vs. control (Con). (B) rWnt3a decreased p-MYPT1 expression, whereas rWnt5a increased it. n = 6 each. *P < 0.05 vs. Con or rWnt5a. (C) Knockdown of Wnt5a with siRNA decreased p-MYPT1 expression relative to the negative control siRNA (siNC) (left), but the addition of rWnt5a markedly reversed it (right). n = 6 each. *P < 0.05. (D) rKlotho (KL) inhibited rWnt5a-induced upregulation of p-MYPT1 in cells with (right) or without siWnt5a (left). n = 6 each. *P < 0.05 vs. Con or rWnt5a + KL. (E) Effects of siWnt5a on Ang II–induced increase in p-MYPT1 expression. siWnt5a significantly decreased basal (third from left) and Ang II–induced (fourth) expression of p-MYPT1, but the decrease was reversed by rWnt5a (fifth); the additional KL again inhibited p-MYPT1 expression (sixth). n = 6 each. *P < 0.05 vs. siNC-Con or siWnt5a + Ang II + Wnt5a. Data are means ± SEM. Unpaired t tests were performed on comparisons between 2 groups. For multiple comparisons, statistical analysis was performed by Tukey-Kramer post hoc test. N.S., not significant.