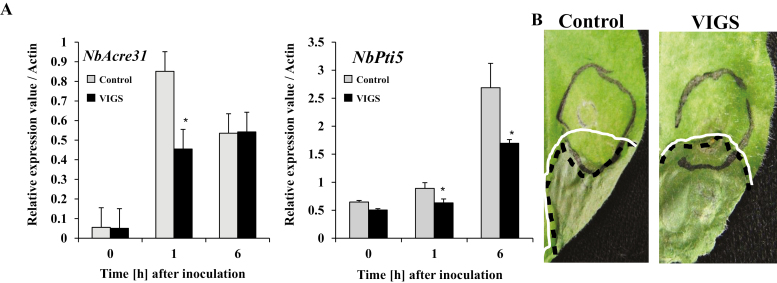
Fig. 7.
Effect of NbPLC2s-silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana on pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-triggered immunity (PTI) in response to Pseudomonas fluorescens (an effective PTI inducer). Leaves of plants at 8 weeks old were infiltrated with P. fluorescens. Plants were silenced using VIGS. (A) Expression of the PTI marker genes NbAcre31 and NbPti5 were determined by qRT-PCR and are relative to the control, with values normalized against Actin. Data are means (±SD) of n=3 replicates. Significant differences between control and VIGS plants were determined using Student’s t-test: *P<0.05. (B) A cell death-based assay for PTI. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci was used as the death-inducible challenger, and P. fluorescens was infiltrated into the leaves to induce PTI (area within grey circle). At 7 h after P. fluorescens inoculation, the same leaves were challenged with P. syringae pv. tabaci (area within the white line). The area within the black dotted line indicates the necrotic lesions caused by P. syringae pv. tabaci. The images were taken 5 d after inoculation with P. syringae pv. tabaci.