Figure. 5.
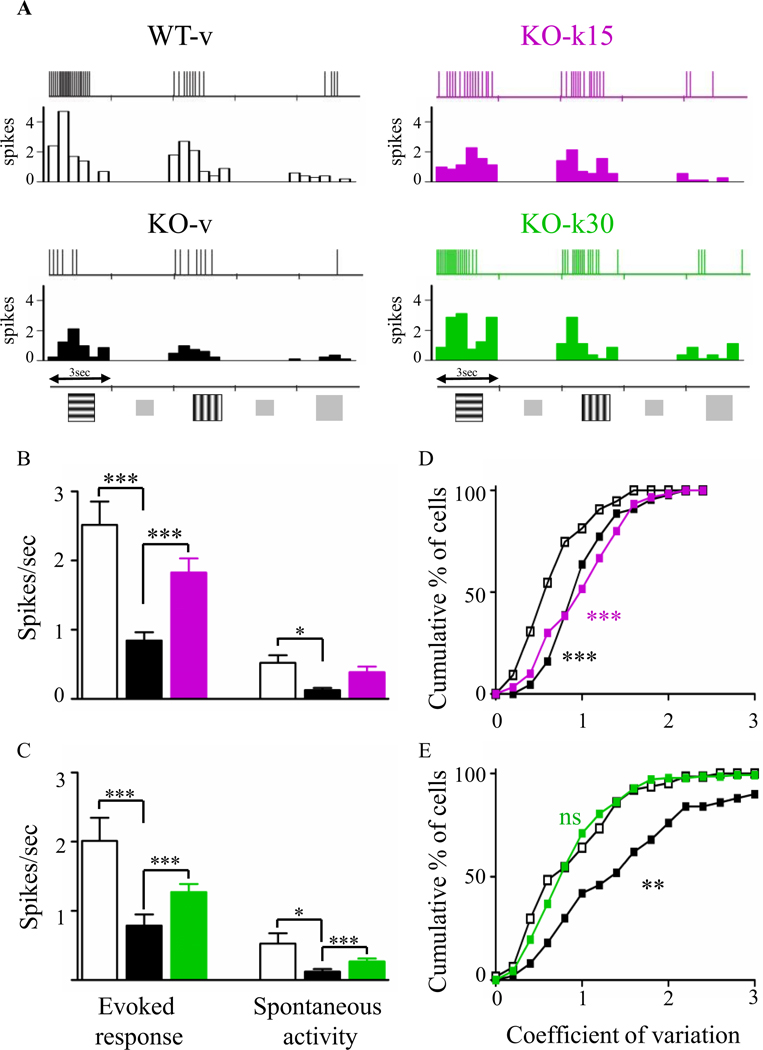
Ketamine increases neuronal activities and response reliability in visual cortex. (A) Representative spike trains and corresponding peristimulus time histogram (PSTH) in response to two oriented gratings or a uniform gray stimulus (8 presentations each). (B, C) Averages of maximal evoked and spontaneous activities. Ketamine treatment significantly increased both types of activity in both treatment paradigms (Kruskal-Wallis, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01,*** p ≤ 0.001, Dunn’s post-test). (D, E) Coefficient of variation of the response to the preferred gratings. Only KO-k30 had a restored coefficient of variation value (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001. WT-v15, n = 74; KO-v15, n = 66; KO-k15, n = 44; WT-v30, n = 57; KO-v30, n = 60; KO-k30, n = 138 cells).
