Fig. 1.
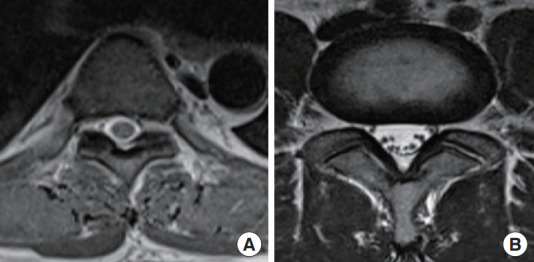
Magnetic resonance imaging pictures comparing the thoracic vertebra (A) and lumbar vertebra (B). Note the difference in size and the distribution of the rootlets and the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, which makes thoracic levels more susceptible to heat injury (less buffer).
