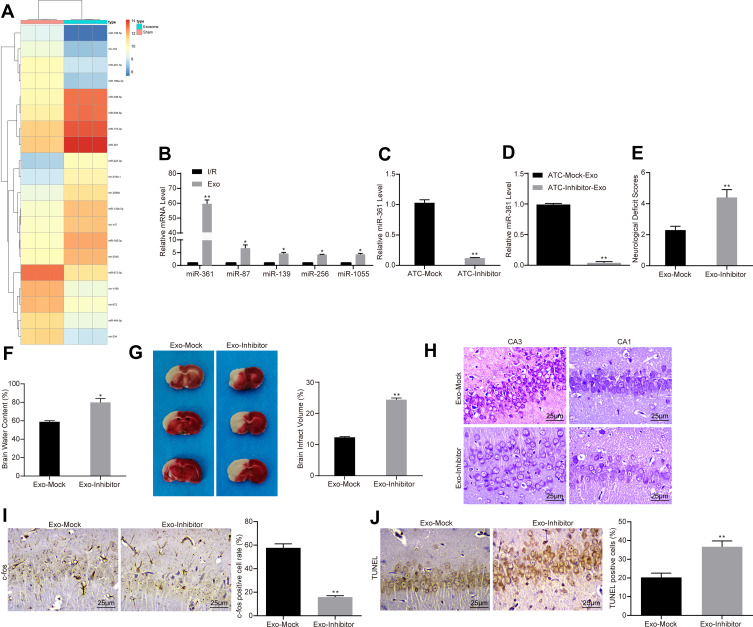
Figure 3.
ATC-derived exosomal miR-361 protects I/R injury. (A) We first used microarray to analyze the expression of differentially expressed miRNAs in PC12 cells treated with ATC-derived exosomes. (B) RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression levels of miR-361, miR-87, miR-139, miR-256 and miR-1055 in PC12 cells to verify the accuracy of transcriptome data. (C, D) Exosomes were extracted after transfection of miR-361 inhibitor or corresponding NC in ATCs. RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of miR-361 in ATCs and exosomes. (E) I/R rats were treated with exosomes transfected with miR-361 inhibitor or empty, at a dose of 30 μg/mL. The effect of the intervention of miR-361 expression on the neurocognitive function of the rats was assessed by neurological deficit score. (F, G) The infarct size and cerebral edema degree of rats treated with miR-361 inhibitor-transfected exosomes were calculated by TTC staining. (H) Nissl staining used to detect the number of Nissl’s body in rat brain tissue. (I) Detection of nerve activity in rats in each group by c-fos immunohistochemistry. (J) Detection of neuronal apoptosis in rats in each group by TUNEL assay. All experiments were performed three individual times; Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test were used to determine statistical significance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs the Exo-Mock group.
Abbreviations: ANOVA, analysis of variance; ATC, astrocyte; Exo, exosome; miR, microRNA; I/R, ischemic-reperfusion; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TTC, 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazole chloride; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end labeling.