FIGURE.
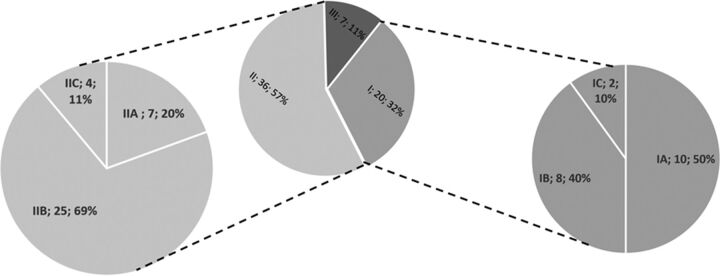
Distribution of reasons for reperfusion failures. Relative frequencies of reasons underlying reperfusion failures. The most common reason was reperfusion failure after intracranial access was established (category II, 36/63). Here, the most common reason was the inability to retrieve the clot despite multiple attempts, stent-retriever failure (IIB). Other reasons in this category group included the inability to pass the clot with the microwire or microcatheter (IIA) or secondary spontaneous/iatrogenic reocclusion after initial reperfusion was established (IIC). Access failures were observed in 20 cases (category I). For further exact definitions of respective subcategories, see the proposed classification scheme outlined in the “Materials and Methods” section.