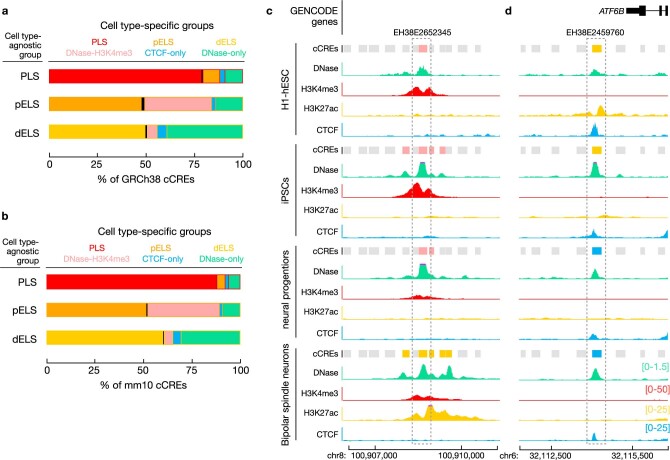
Extended Data Fig. 1. Classification of human cCREs is largely consistent across biosamples.
a, b, For the 25 human (a) and 15 mouse (b) biosamples that were covered by all four core assays, we analysed how cCRE classification could differ between biosamples. For each cell-type-agnostic group of cCREs, the bars indicate their group classification in specific biosamples, coloured by group as indicated. Black indicates a switch in the grouping, for example, from cell type-agnostic PLS to cell type-specific pELS or CTCF-only. c, d, Two example switches of cCRE grouping between different biosamples. c, EH38E2652345 is a cCRE-dELS that has high DNase, H3K4me3, and H3K27ac signals in bipolar spindle neurons. By contrast, in cell types at earlier stages of neuronal differentiation, such as embryonic stem cells, iPSCs, and neural progenitor cells, this cCRE only has high DNase and H3K4me3 signals, suggesting that in these cell types the cCRE may be a poised enhancer. d, EH38E2459760 is a cCRE-dELS that has high DNase, H3K27ac, and CTCF signals in H1-hESCs and iPSCs. However, in further differentiated cell types such as neural progenitors and bipolar spindle neurons, the H3K27ac signal decreases while the CTCF signal remains, and accordingly, EH38E2459760 is classified as a CTCF-only cCRE. In c and d, cCRE colours correspond to group classification defined in a and b. Grey cCREs have low DNase signals.