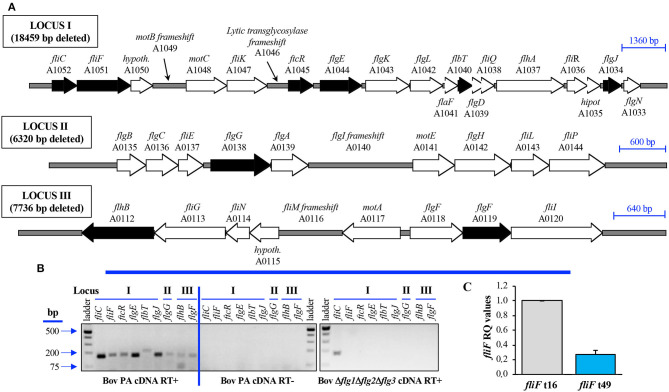
Figure 1.
Genomic organization (A) and transcription (B,C) of the three main flagellar loci detected in the B. ovis genome. Flagellar genes targeted in transcription analysis with B. ovis PA strains (B,C) are represented with a black pattern (A). Mutagenesis procedure deleted 99% of each locus (A) in flagellar mutants listed in Table 2. End-point RT-PCR (B) was performed with cDNA obtained by retrotranscription of RNA extracted at t16 from B. ovis PA or the Δflg1Δflg2Δflg3 triple mutant (RT+ reactions). Reactions of cDNA synthesis lacking RT were used as controls of DNA absence (RT- reactions). Amplification with fliC primers in the Δflg1Δflg2Δflg3 triple mutant (B) was expected, since both primers hybridize adjacent but externally to the deleted fragment (the deletion removes 80% of fliC). qRT-PCR (C) with fliF was performed with RNA extracted at t16 and t49 from B. ovis PA parental strain. Gene expression levels (C) were determined, with the StepOneTM software v2.3, by the 2−ΔΔCt method with the 16S gene as internal reference and t16 results as control condition. Four biological replicates, with three technical replicates each, were analyzed and the results are expressed as means ± SD.