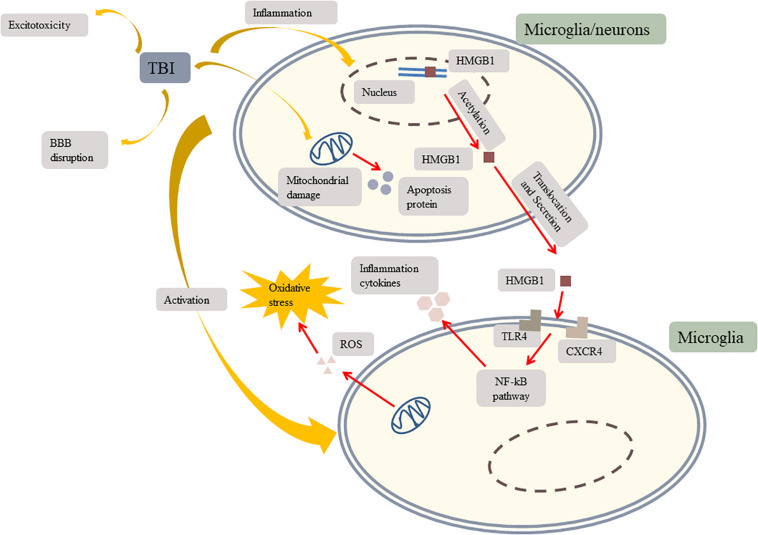
FIGURE 2.
TBI induces inflammation, mitochondrial damage, microglial activation, excitotoxicity, and BBB disruption. TBI results in HMFB1 translocation and secretion. Extracellular HMGB1activates TLR4 and CXCR4 to trigger the NF-kB pathway which induces microglia secreting inflammation cytokines to further activate other microglia. TBI induces mitochondrial damage. Damaged mitochondria produce apoptosis protein and ROS to aggravate oxidative stress. Besides, TBI leads to excitotoxicity and BBB disruption which makes inflammation cytokines leakage more severe. TBI, traumatic brain injury; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; CXCR4, chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4; BBB, blood–brain barrier; HMGB1, high-mobility group box 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; ROS, reactive oxygen species.