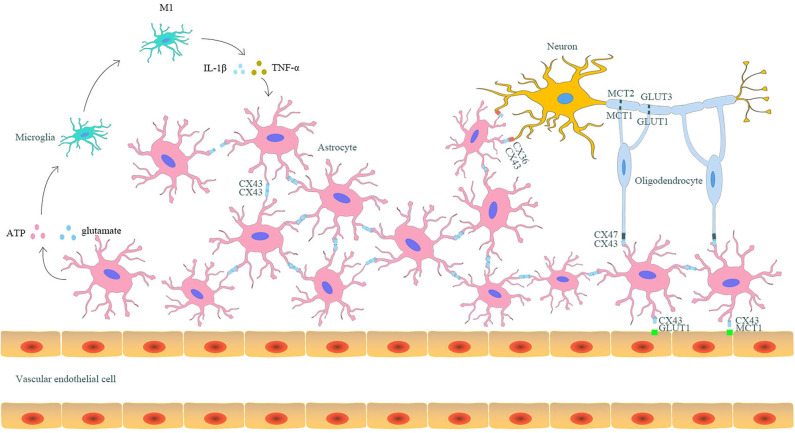
Figure 1.
The interaction between astrocytic Cx43 and other parenchymal cells in the CNS. Astrocytes and other parenchyma cells in the CNS form neuro–glial syncytium structures via Cx43/Cx43 gap junctions between astrocytes, Cx43/Cx36 gap junctions between astrocytes and neurons, and Cx43/Cx47 gap junctions between astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Such structures allow the exchange of metabolites and rapid signal communication, resulting in synergistic response to stimuli. Astrocytic Cx43 is also involved in the capillary-astrocyte-oligodendrocyte-neuron axis and participates in the lactate and glucose transport between capillaries and neurons. Moreover, astrocytes can also indirectly promote the differentiation of microglia to the M1 phenotype through releasing pro-inflammatory mediators via hemichannels. In turn, the differentiated M1 microglia could aggravate the destruction of gap junctions, enhancing injury after ischemic stroke.