Figure 5.
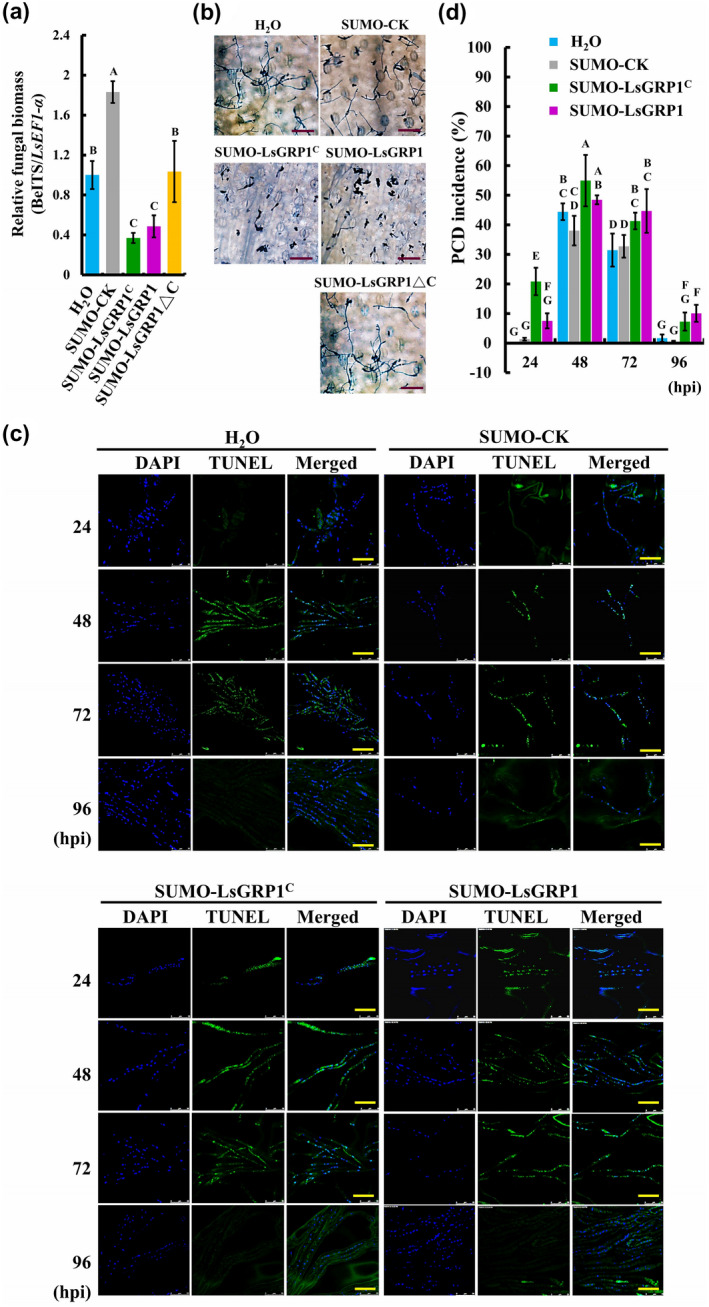
Increasing LsGRP1C abundance in leaves promotes grey mould resistance of lily by enhancing fungal apoptosis programmed cell death (PCD). Lily leaf disks were infiltrated with 10 μM protein solution of SUMO‐LsGRP1C, SUMO‐LsGRP1, SUMO‐LsGRP1ΔC, or control protein of SUMO fusion partner (SUMO‐CK) and droplet‐inoculated with a 10‐μl spore suspension of Botrytis elliptica at 5 × 104 spores/ml 1 hr later. Relative biomass (a) and in planta growth (b) of B. elliptica were detected by quantitative PCR and trypan blue staining, respectively, at 24 hours post‐inoculation (hpi). (c) Total fungal nuclei and the nuclei undergoing chromosomal DNA fragmentation were detected by 4′,6′‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI) staining and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end‐labelling (TUNEL) staining, respectively. (d) The incidence rate of fungal apoptosis PCD was calculated based on the ratio of TUNEL‐labelled nuclei to DAPI‐labelled nuclei. Sterile deionized water (H2O) was used instead of protein solutions as a negative control. Data represent the mean ± SD of three biological replicates. Statistics analysis was performed using analysis of variance followed by LSD test (p < .05). Bar: 100 μm in (b); 25 μm in (c)
