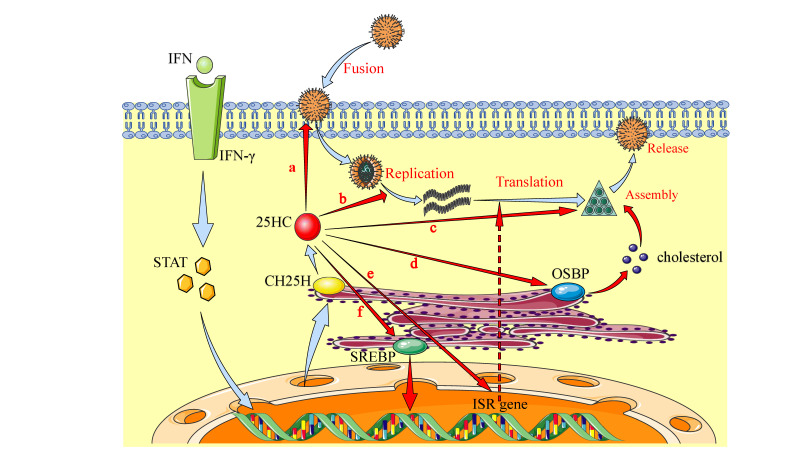
Figure 3.
Broadly antiviral activities of 25HC through multiple mechanisms. The expression of CH25H can be induced through interferon receptor (IFNR) signaling, and then the production of 25HC is promoted from converting cholesterol. Studies have showed that CH25H and 25HC are involved in broadly antiviral activity via various mechanisms, including a, Inhibition of virus adsorption and entry by decreasing the cholesterol level of plasma membrane lipids; b, Inhibition of viral genome replication; c, Antagonizing prenylation of viral and endogenous protein that is involved in viral replication and assembly; d, Interactions with oxysterol-binding proteins to alter the cholesterol distribution; e, Activation of the gene expression associated with the integrated stress response (ISR) in macrophages, increasing oxidative stress and translation suppression; and f, Regulation of inflammation, innate immunity, and adaptive immunity.