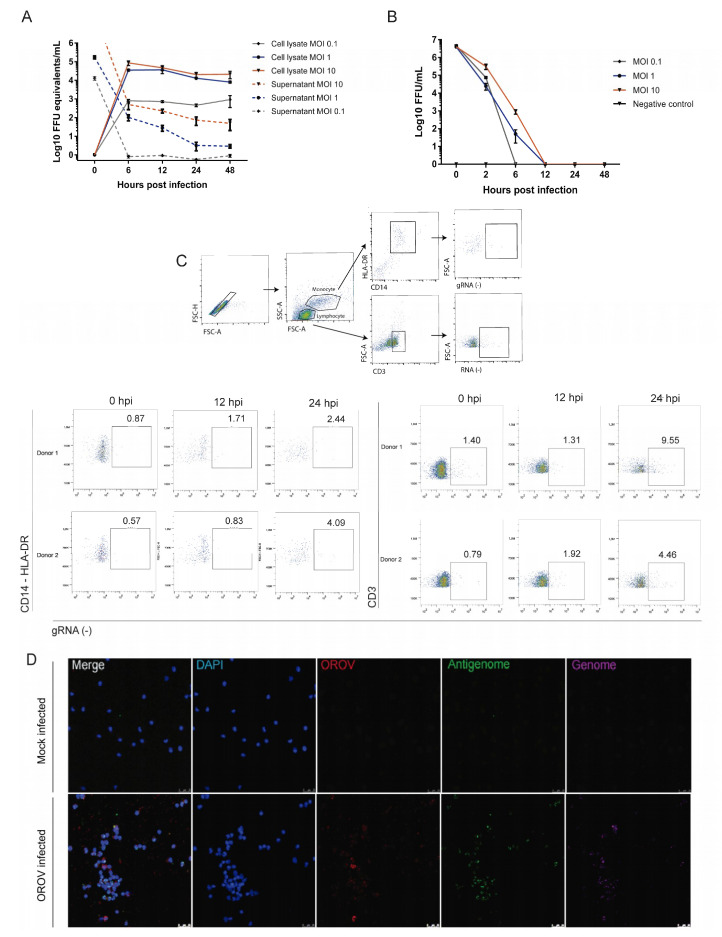
Figure 3.
Human peripheral blood monocytes and lymphocytes are susceptible to OROV infection but generate low yields of infectious particles. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were obtained from whole blood of healthy donors, infected in vitro and analyzed by different methodologies. (A) PBMCs were seeded in 24-well plates and infected with OROV MOI 0.1; 1 and 10. Cell lysates and supernatants were collected to RNA quantification by qRT-PCR (n = 3). (B) The supernatants were also analyzed by FFA assay. Symbols represent the mean of viral load ± SEM. (C) PBMCs from healthy donors (n = 2) were infected with MOI 1, submitted RNA PrimeFlow™ protocol 24 hpi and flow cytometry. CD3+ and CD14+ HLA DR+ percentage of events with OROV Grna, and the gating strategy are shown. (D) Detection of OROV 48 hpi in cells infected with MOI 2, by confocal microscopy. OROV proteins in red (Alexa Fluor 594); genome (gRNA) in magenta (AlexaFluor 647); antigenome (agRNA) in green (AlexaFluor 488); DAPI (blue). Images with 63x times magnification. Scales at 25 μm.