Figure 2.
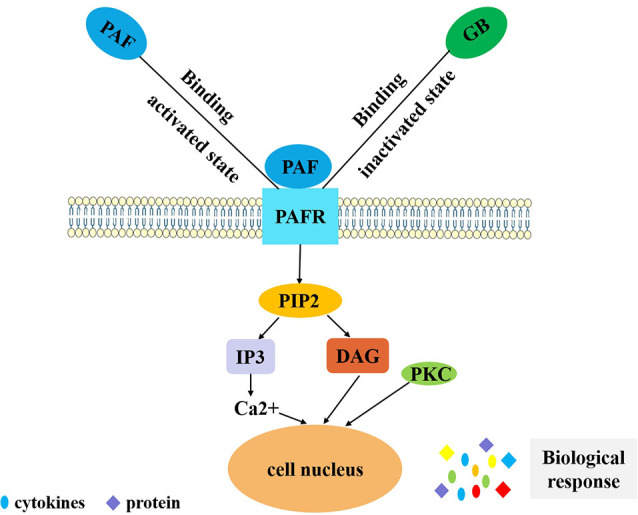
PAF-mediated signal transduction of ginkgolides in the regulation of IIR. PAF binds to PAF receptor in vivo, and coupled with G protein, phospholipase C is activated and has an effect on phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate breakdown produces inositol triphosphate and diglyceride. Inositol triphosphate can induce intracellular calcium concentration increases and diglyceride can activate PKC. Finally, it exerts a biological effect by secreting cytokines and proteins. GB competitively inhibits PAF binding to PAFR in order to reduce the above series of reactions and play an anti-inflammatory role. PAF, platelet-activating factor; IIR, inflammatory immune response; PKC, protein kinase C; GB, ginkgolide B.PAF, platelet-activating factor; PAFR, platelet-activating factor receptor; GB, ginkgolide B; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; IIR, inflammatory immune response.
