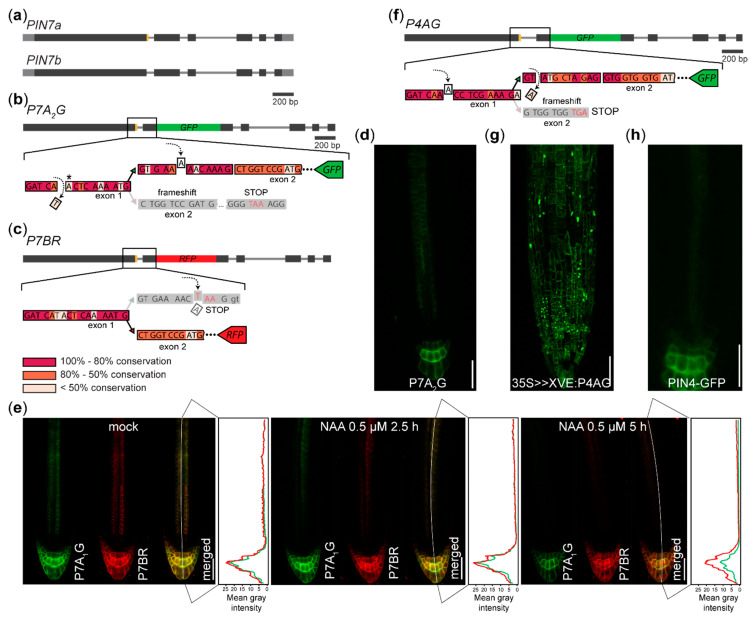
Figure 2.
Reporters visualizing AS of PIN7 and PIN4 in the root tip: (a) Diagram of the coding regions of the PIN7 gene. The canonical PIN7b isoform differs from PIN7a in the presence of the 12 nucleotide region (orange). (b) Scheme of the P7A2G reporter for visualizing the PIN7a isoform. Removing the nucleotide prior to the alternative splice site leads to a frameshift in the PIN7b transcript. The frame is restored by insertion of the nucleotide into the region exclusively encoded in the P7A2G sequence following the alternative splice site. Asterisk: a neighboring A nucleotide is removed in the P7A1G sensor [10] (c) The P7BR reporter, as outlined in [10]. The visualization of P7BR is accomplished by introducing the termination codon into the protruding region encoded entirely by PIN7a. P7AG and P7BR are encoded by two constructs that are separately transformed and then crossed. (d) Expression pattern of the P7A2G reporter. (e) Following the treatment with the synthetic auxin NAA, a differential decrease of expression is observed in the root columella cells, while nearly no difference in their expression change is observed in the vascular cylinder. (f) Scheme of the P4AG reporter for visualizing the PIN4a isoform (PIN4 shows an identical exon/intron structure with PIN7 [16]). Following the induction of the 35S>>XVE:P4AG transgene, the GFP fluorescence is also seen outside (g) the PIN4:PIN4-GFP expression domain (h). Bars, 100 µm on (e), (d), (g) and (h). Black—coding regions, grey—UTRs, thin grey line—introns, yellow—regions modified by AS, red—RFP, green—GFP on (a), (b), (c) and (f). The color shading of the evolutional conservation code outlined (c) was assessed as a percentage of the preserved nucleotides on the alignment of the PIN7-like sequences within the Brassicaceae family.