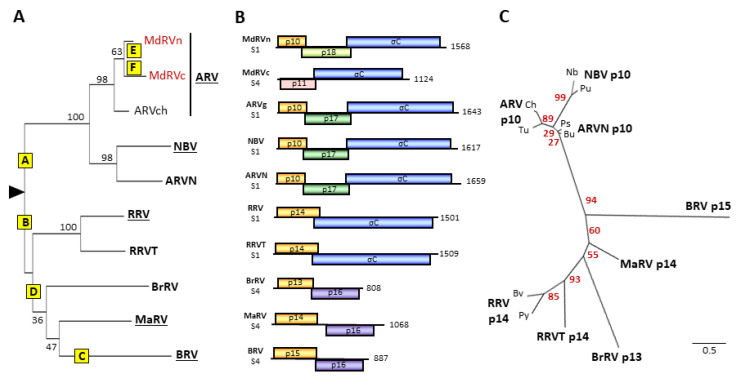
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of fusogenic orthoreoviruses and FAST proteins and comparisons of their polycistronic genome segments. (A) Maximum likelihood unrooted phylogram of the sigma-class outer capsid clamp proteins of the eight fusogenic orthoreovirus species. The tree with the highest log likelihood is shown and included 10 amino acid sequences. See Supplementary Table S2 for a list of viruses, host species, and accession numbers The ARV species included single isolates from three subgroups, chickens (ARVch) and classical (MdRVc) and novel (MdRVn) MdRVs. Bootstrap values (500 replicates) indicating the percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together are shown next to the branches. Branch lengths are to scale and measured by the number of substitutions per site. Yellow boxes labeled A–F indicate predicted genetic events leading to the extant species, as described in the text: A—recombinant gain of p10 FAST protein precursor; B—recombinant gain of p13/p14 precursor; C—potential recombinant gain of p15 precursor; D—recombinant gain of p16 and loss of fiber proteins; E—point mutations ablate p10 function; F—recombinant loss of p10 FAST protein. (B) Diagrams of the polycistronic S1 and S4 genome segments, drawn to approximate scale, of the indicated eight species or proposed species of fusogenic orthoreoviruses, plus the MdRVc (MdC) and MdRVn (MdN) subgroups of non-fusogenic ARVs from waterfowl. Open reading frames are depicted by rectangles, labeled to indicate the protein product and color-coded to depict functional or evolutionary protein relationships: yellow—FAST protein; blue—fiber protein; green—potential cell cycle inhibitory protein; purple—homologous proteins with no defined function; pink—heterologous nonfusogenic protein of no defined function. Numbers refer to mRNA length. (C) Maximum likelihood unrooted phylogram of the FAST proteins encoded by the indicated eight species or proposed species (boldface) of orthoreoviruses. The tree with the highest log likelihood is shown and included 14 amino acid sequences. See Supplementary Table S3 for a list of viruses, host species, and accession numbers. Lowercase labels denote isolates within a species: Ch and Tu are chicken and turkey isolates of ARV; Bu and Ps are bulbul and psittacine isolates of ARVN; Nb and Pu are the prototype NBV and Pulau isolates of NBV; Bv and Py are the bush viper and python isolates of RRV. Bootstrap values (500 replicates) indicating the percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together are shown next to the branches. Branch lengths are to scale and measured by the number of substitutions per site.