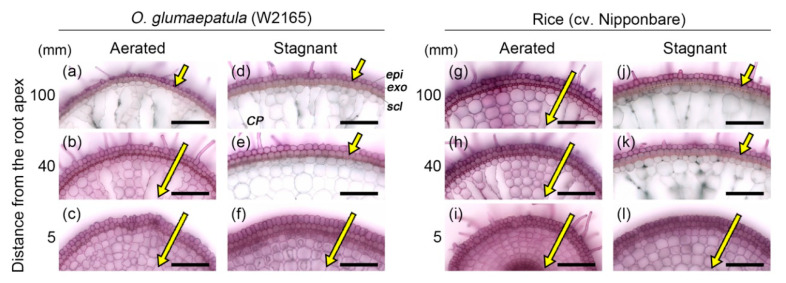
Figure 4.
Permeability of the outer part of roots to an apoplastic tracer (periodic acid) in accession W2165 of O. glumaepatula and rice (cv. Nipponbare) under aerated or stagnant conditions. The permeability of the exodermis was evaluated at the basal parts (95–105 mm from the root apex; (a,d,g,j), middle parts (35–45 mm from the root apex; (b,e,h,k) and root tips (2.5–7.5 mm from the root apex; (c,f,i,l) of adventitious roots of 115–120 mm length. Purple color indicates that periodic acid penetrated into root tissues. The length of yellow arrows indicates the extent of penetration. Plants were grown in aerated nutrient solution for eight days and then transferred to deoxygenated stagnant 0.1% agar solution or continued aerated solution for 13–15 days. CP, cortical parenchyma; epi, epidermis; exo, exodermis; scl, sclerenchyma. Scale bars: 100 μm.