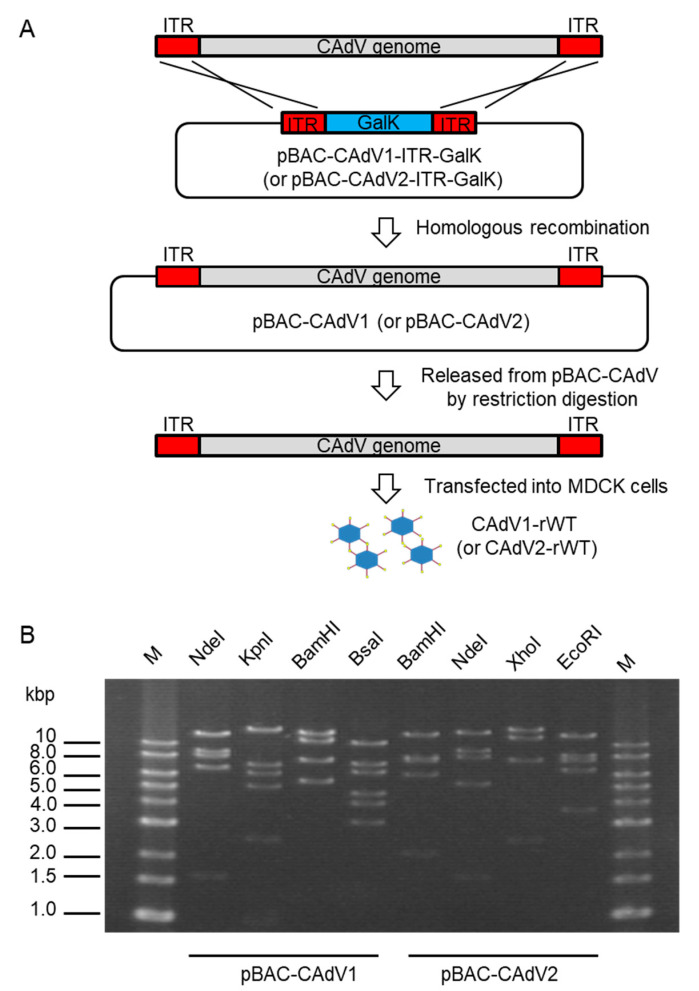
Figure 1.
Cloning of canine adenovirus (CAdV) genomes into bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) vectors. (A) CAdV1 (or CAdV2) DNA was introduced into SW102 cells harboring pBAC-CAdV1-ITR-GalK (or pBAC-CAdV2-ITR-GalK). The plasmid contains a galactokinase (galK) expression cassette flanked by approximately 50 bp of inverted terminal repeats (ITR) of the viral genome. After homologous recombination by Red recombinase, cells were selected using GalK, and pBAC-CAdV1 (or pBAC-CAdV2) was obtained. Then, this plasmid was digested with a restriction enzyme and transfected into Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells, following which the recombinant virus CAdV1-rWT (or CAdV2-rWT) was rescued. (B) Restriction enzyme analysis of pBAC-CAdV1 and pBAC-CAdV2. pBAC-CAdV1 was digested with NdeI, KpnI, BamHI, and BsaI, whereas pBAC-CAdV2 was digested with BamHI, NdeI, XhoI, and EcoRI. The predicted molecular weights of the digested fragments of pBAC-CAdV1 are 13099, 8710, 8038, 6737, and 1603 bp for NdeI; 16319, 7077, 6210, 5110, 2490, and 981 bp for KpnI; 13573, 10982, 7620, 5549, and 463 bp for BamHI; and 10530, 7212, 6386, 4670, 4041, 3117, 825, 493, 471, 153, 147, and 142 bp for BsaI. The predicted molecular weights of the digested fragments of pBAC-CAdV2 are 13521, 7998, 7620, 6151, 2109, 851, and 722 bp for BamHI; 14820, 9059, 8127, 5363, and 1603 bp for NdeI; 16628, 12194, 7688, and 2462 bp for XhoI; and 13014, 8192, 7592, 6532, and 3642 bp for EcoRI. M: 1-kb DNA ladder marker.