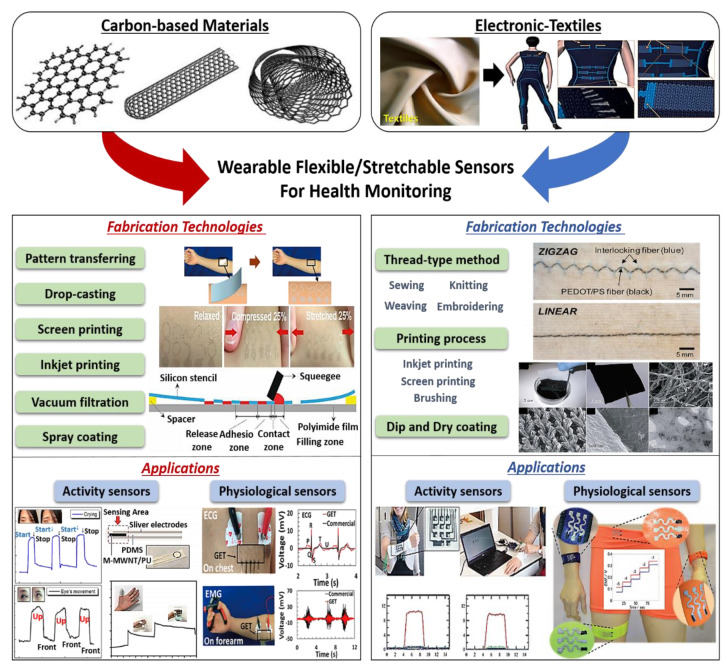
Figure 1.
Schematic of effective approaches for wearable flexible/stretchable sensor applications in health monitoring: (i) Carbon-based materials (reproduced with permission [25] copyright 2008, American Chemical Society) and (ii) Electronic textiles (e-textiles) (reproduced with permission [21] copyright 2014, Royal Society of Chemistry). Fabrication technologies; screen printing (reproduced with permission [31] Copyright 2015, Wiley-VCH), pattern transferring (reproduced with permission [30] copyright 2017, American Chemical Society), dipping and drying (reproduced with permission [32] copyright 2010, American Chemical Society), weaving (Reproduced with permission [33] copyright 2017, American Chemical Society). Applications using carbon-based materials; activity sensors: strain sensor (reproduced with permission [34] copyright 2015, American Chemical Society) and pressure sensor (reproduced with permission [35] copyright 2018, MDPI AG). Physiologic sensors: electrocardiogram (ECG) and electromyogram (EMG) sensor (reproduced with permission [30] copyright 2017, American Chemical Society). Applications using e-textiles; activity sensors: capacitive-type pressure sensor (reproduced with permission [36] copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH). Physiologic sensors: a textile-based wearable multi-ion potentiometric sensor (reproduced with permission [37] copyright 2017, Wiley-VCH).