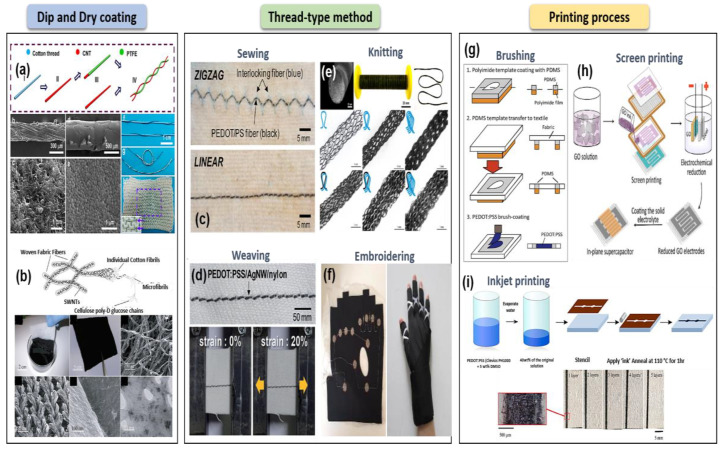
Figure 6.
Fabrication technologies for textile-based wearable sensors. Dip and dry coating; (a) fabrication of fiber-based electronics with CNT-coated cotton thread (CCT) using a dipping and drying process (reproduced with permission [107] copyright 2014, American Chemical Society). (b) The SWCNT-coated woven polyester fabric using an extremely simple dipping and drying process (reproduced with permission [32] copyright 2010, American Chemical Society). (c) Optical images of zigzag- and linear-type PEDOT/PS fiber embedded fabrics by sewing method (reproduced with permission [33] copyright 2017, American Chemical Society). (d) Woven sensor fabric fabricated by weaving process (reproduced with permission [118] copyright 2017, Royal Society of Chemistry). (e) PU/PEDOT:PSS fibers co-knitted with a commercial Spandex yarn using knitting method (reproduced with permission [121] copyright 2015, American Chemical Society). (f) Textile-based smart gloves realized by the embroidering method (reproduced with permission [122] copyright 2017, Informa UK Limited). Printing process; (g) schematics of the fabrication process of brush-painted PEDOD:PSS electrode on knitted fabrics using PDMS-made stencil (reproduced with permission [125] copyright 2015, Nature Publishing Group). (h) Screen-printed rGO electrode on woven cotton fabrics through the strong chemical interaction between GO and cotton fibers (reproduced with permission [126] copyright 2017, IOP Publishing). (i) Patterning PEDOT:PSS on PET nonwoven fabric using inkjet printing and sponge stencil (reproduced with permission [128] copyright 2016, American Chemical Society).