Figure 1.
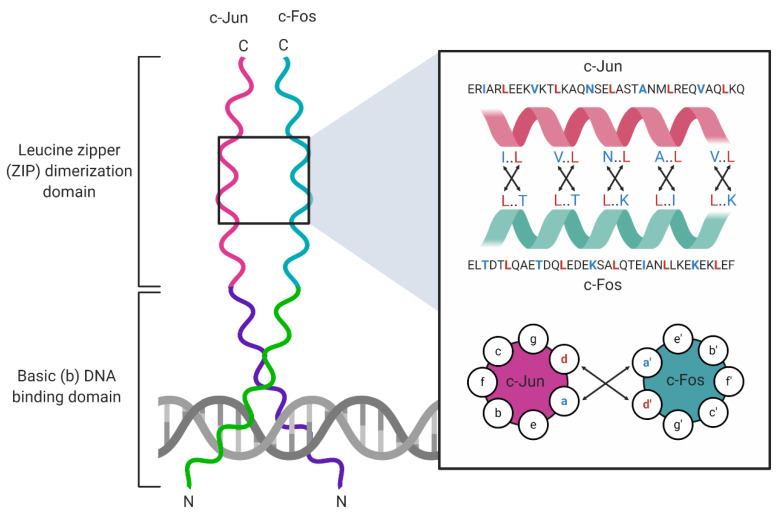
Structure of the c-Jun/c-Fos heterodimer. The c-Jun/c-Fos complexes bind DNA as heterodimers. Each bZIP protein contains a leucine zipper (ZIP) and adjacent basic (b) DNA-binding domain that together constitute the bZIP domain. The ZIP domain organizes into heptad repeats with amino acid residues denoted as positions a–g. Hydrophobic interactions (black arrows) between a (blue) and d (red) residues stabilize dimer formation [6]).