Figure 4.
Diverse Mechanisms of Cancer-Related lncRNAs
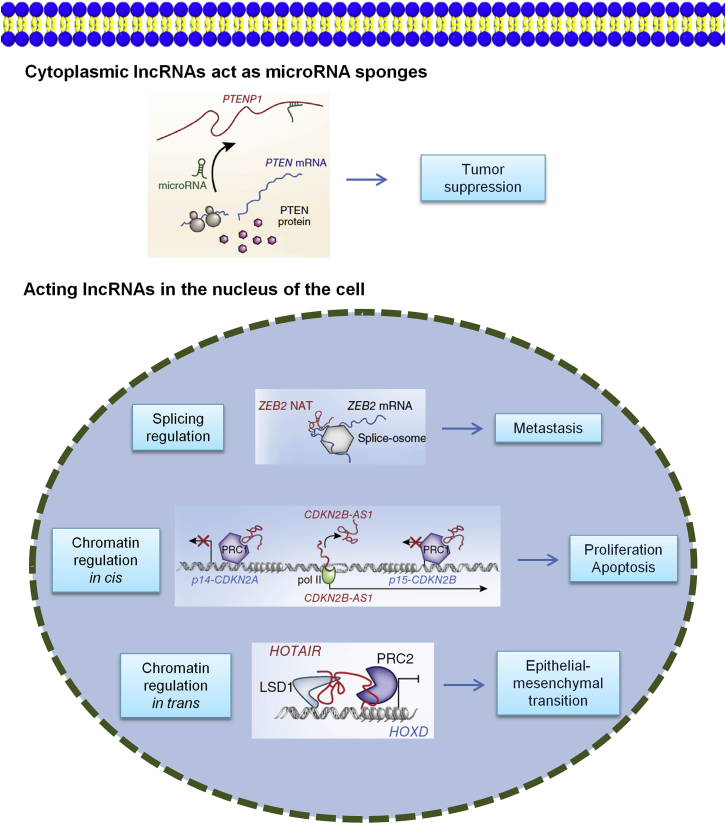
Acting in the nucleus of the cell, some lncRNAs affect the expression of proximally located genes, such as ANRIL (CDKN2B-AS1), which mediates the epigenetic silencing of two genes on the same locus, CDKN2A and CDKN2B, inducing cell proliferation. HOTAIR promotes metastasis in breast cancer by targeting distant genes, such as those in the HOXD cluster, for epigenetic silencing by the PRC2 complex. Other nuclear lncRNAs act post-transcriptionally, such as the NAT of ZEB2 mRNA, ZEB2. The ZEB2 NAT blocks splicing of ZEB2 mRNA, promoting the use of an internal ribosome entry site for translation initiation and delivering high ZEB2 protein levels, which induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. In contrast, a number of cytoplasmic lncRNAs may act as microRNA sponges. For instance PTENP1 binds to microRNAs that otherwise bind to the 3′ untranslated region of PTEN mRNA, reducing its expression and tumor suppressor activity.