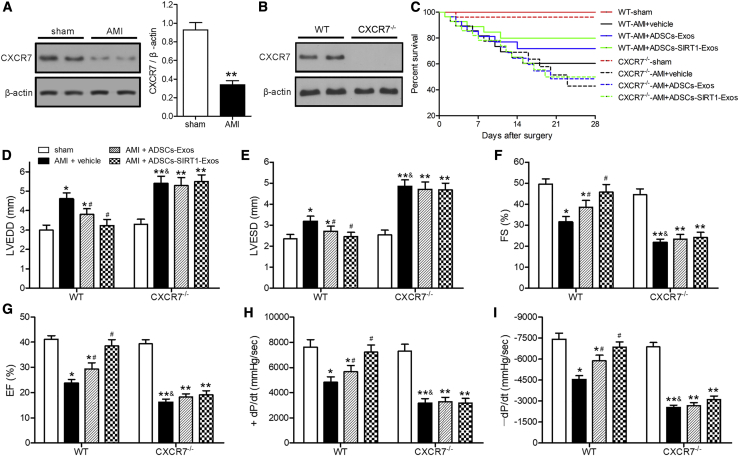
Figure 5.
Injection of Exosomes from ADSCs Overexpressing SIRT1 Helped Restore Cardiac Function in AMI of WT mice but Not in CXCR7−/− Mice
AMI was produced by surgical ligation of the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery. LAD artery ligation or sham surgery was performed in mice; injection of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; vehicle), ADSCs-Exos, or ADSCs-SIRT1-Exos was performed after AMI surgery, and myocardial tissue samples were collected at 28 days after surgery. (A and B) Western blot analyses of the expression levels of CXCR7. The CXCR7 levels were normalized to β-actin. ∗p < 0.05, compared with the sham group. (C) Survival analysis of mice treated as indicated each day after surgery. (D–I) Echocardiographic and hemodynamic measurements of the left ventricular enddiastolic dimension (LVEDD) (D); left ventricular endsystolic dimension (LVESD) (E); fractional shortening (FS) (F); ejection fraction (EF) (G); rates of maximal rise in left ventricular pressure (+dP/dt) (H); and the rate of maximal fall in left ventricular pressure (−dP/dt) (I). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, compared with the sham group; #p < 0.05, compared with the AMI + vehicle group of WT mice; &p < 0.05, compared with the AMI + vehicle group of WT mice; n = 6 per group.