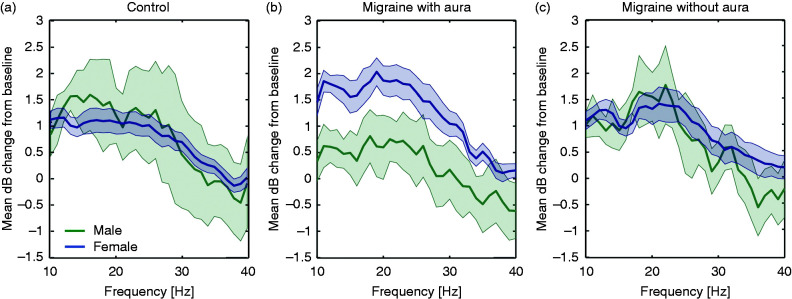
Figure 4.
Gender effect within the overall response power, assessed per stimulation frequency as mean (± standard error) decibel (dB) change from baseline, for controls (a), migraine with aura (b) and migraine without aura (c) subjects. Female migraine patients with aura showed a tendency to more pronounced response to chirp stimulation compared to males. However, this difference did not reach statistical significance (interaction group and gender with respect to low, medium and high frequency windows, all p> 0.06).