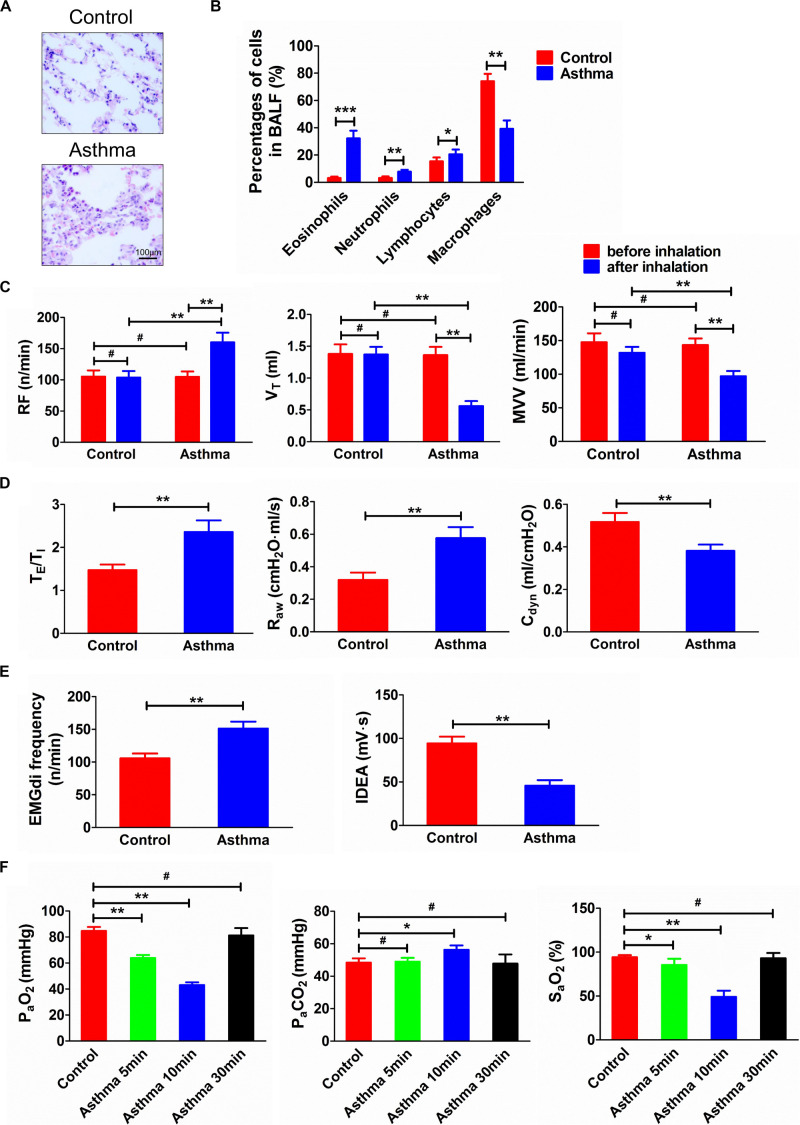
FIGURE 1.
(A) Histopathological changes of lung tissues in asthma and control rats. (B) Percentage of cells in BALF in asthma and control rats. (C) Changes of RF, VT, and MVV before and after challenge. (D) TE/TI, Raw, and Cdyn in asthma and control rats. (E) EMGdi frequency and IDEA in asthma and control rats. (F) Changes of PaO2, PaCO2, and SaO2 in control and asthma (5, 10, and 30 min) rats. After the rats were challenged, the lung function was deteriorated and the relevant indicators of ventilation function were significantly changed. Meanwhile, the airway inflammation, especially the eosinophils in BALF, was significantly increased. At the same time, as the duration of an asthma attack increased, arterial oxygen saturation was decreased. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and #p>0.05, respectively. n = 6 per group. BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; RF, respiratory frequency; VT, tidal volume; MVV, minute ventilation volume; TE/TI, expiratory time course/inspiratory time course ratio; Raw, airway resistance; Cdyn, dynamic pulmonary compliance; EMGdi frequency, frequency of diaphragmatic electric activity; IDEA, integrated diaphragmatic electrical activity.