Figure 3.
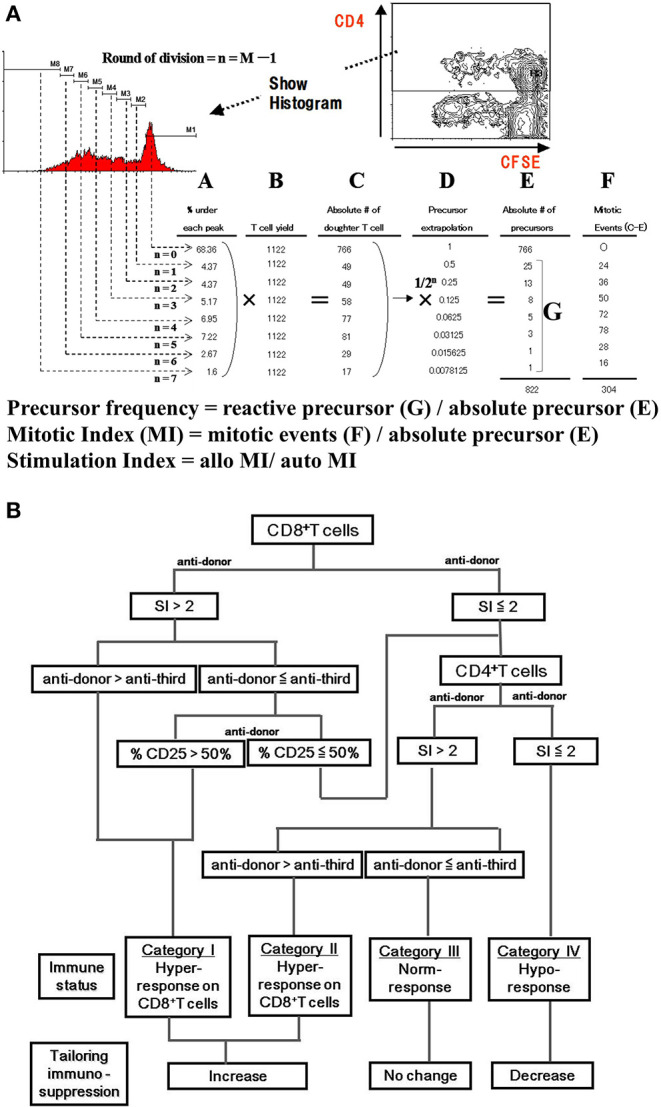
CFSE-MLR for immune monitoring in transplantation. (A) Intensity-based analysis of mixed lymphocyte reaction assay with CFSE dye (CFSE-MLR) provide quantitative estimation of the alloresponse. In brief, the plot and histogram show the gating strategy for CD4+ proliferating cells. Cell division are gated by the rationale that the CFSE fluorescence intensity shows the half-value from former generation. (A) Percentage of CD4+ T cell events in each division, (B) T cell yield, (C) the number of daughter T cells that had divided n times (A multiply B), (D) precursor extrapolation Using mathematical relationship, the number of division precursors (E,G) is extrapolated from the number of daughter cells of each division and from mitotic events (F). These values are used to calculate precursor frequency and mitotic index (MI). As normalized quantitative estimation, stimulation index are calculated by dividing MIs of allogeneic combinations by MIs of autologous controls. (B) Algorithm to estimate anti-donor alloreactivity in liver transplant recipients. The immune reactivity of liver transplantation recipients is classified into four categories. By analyzing the proliferation and CD25 expression of the CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subsets in response to anti-donor and anti-third party stimuli, the immune status is categorized as hypo-, normo-, or hyper-responsive. In recipients with hyper-response on either CD4+ or CD8+ T cells, immunosuppressants consider to be increased. In patients with normo-response, immunosuppressant tapering is abandoned. Only in patients with hypo-response, immunosuppressant therapy can be tapered off (98). SI, stimulation index.
